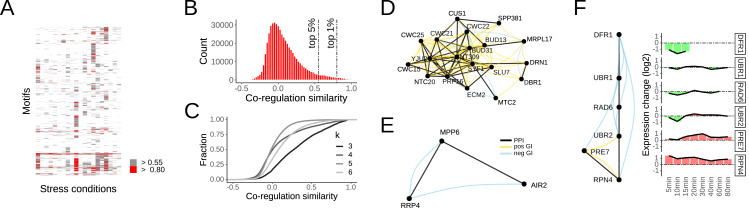
Figure 5. Transcriptional co-regulation of FNMs in response to environmental perturbations.
(A) Heatmap of co-regulation expressed through average pairwise cosine similarity of the expression profiles of the individual nodes in the motif. The top 5% and 1% are color coded. Rows of motifs with no co-regulation in at least the top 5% are not shown. (B) Distribution of the FNM co-regulation scores. The top 5% and 1% are indicated in the far right tail of the distribution. (C) Cumulative distribution curves of the co-regulation scores as function of motif size k. (D) An exemplary cluster of motifs that is strongly transcriptionally co-regulated during heat stress identifies the core splicing machinery. (E) An exemplary FNM that is strongly co-regulated during heat stress highlights extensive cross-talk between RNA surveillance and quality control. (F) An FNM that connects the transcription regulatory network to the metabolic network may indicate a regulatory function of the E2-E3 complexes formed by RAD6, UBR1 and UBR2 in coupling transcript and protein levels during heat stress.