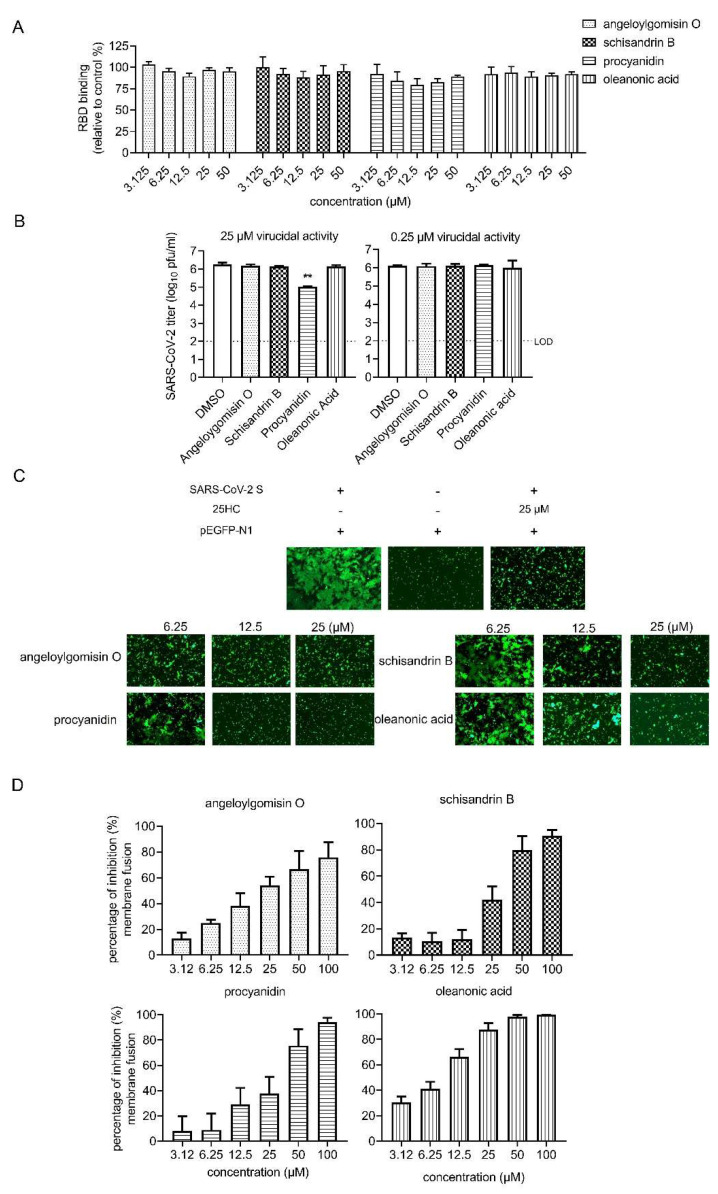
Figure 4.
Effects of four hits on different stages of SARS-CoV-2 entry. (A) Effect of four hits on the binding between ACE2 and SARS-CoV-2 RBD. SARS-CoV-2 RBD was coated on the 96-well plates, followed by incubation with hACE-his in the different concentrations of the four hits or vehicle (DMSO) for 1 h. After washing with PBS, the HRP-conjugated anti-his antibody was incubated with the plates. After adding a color reagent for 15 min, the OD450 was measured, and the efficiency of RBD binding was normalized with the vehicle control. (B) Result of the virucidal assay. (Left) SARS-CoV-2 was incubated with DMSO or the hits (25 μM for 1 h). The treated virus was determined by the plaque assay. (Right) SARS-CoV-2 was incubated with DMSO or the hits (0.25 μM for 1 h). (C) SARS-CoV-2 S (ct19)-mediated cell–cell fusion on Vero E6 cells. (Left) Vero E6 cells that were co-transfected with SARS-CoV-2 S (ct19) and GFP plasmid. (Middle) Cells were transfected with GFP. (Right) Cells were co-transfected with SARS-CoV-2 S (ct19) and GFP and treated with 25-μM 25HC. Four hits inhibited SARS-CoV-2 S (ct19)-mediated membrane fusion in a dose-dependent manner. (Bottom) Vero E6 cells were co-transfected with SARS-CoV-2 S (ct19) and GFP later treated with the four hits in different concentrations. Syncytium formation was visualized 24–36 h later using fluorescent microcopy. Images are representative fields from three independent experiments. (D). Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 S (ct19) protein-mediated cell–cell fusion by the inhibitors, determined by a DSP-based cell fusion assay. The effector cells were co-transfected with SARS-CoV-2 S (ct19) and a DSP1-7 plasmid, and the target cells were transfected with DSP8-11 plasmid. The cell fusion activity was quantitatively determined by measuring the luciferase activity. Data are presented as the means ± standard deviations (SDs) for more than 2 independent experiments (** p < 0.01).