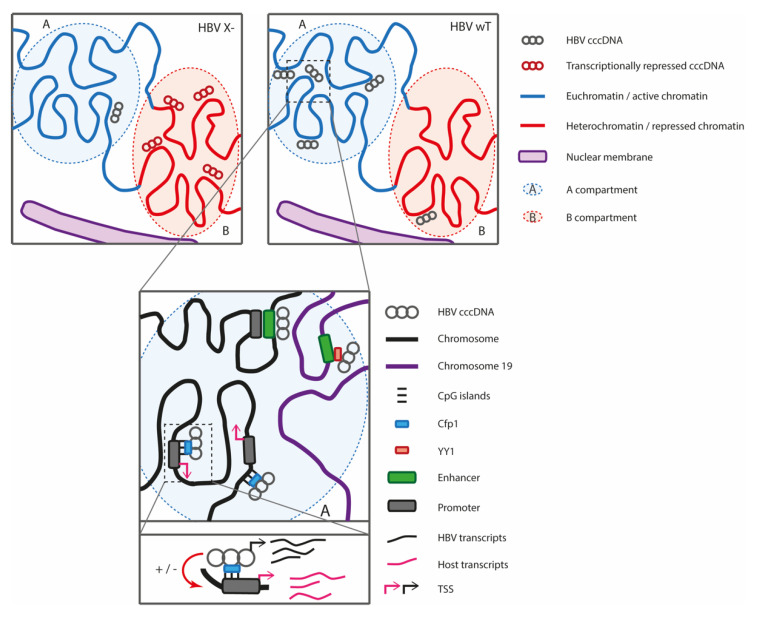
Figure 2.
Graphical summary of HBV interactions with 3D genome. HBV cccDNA in cells infected with a wild-type virus (HBVwt) is preferentially associated with active chromatin and compartment A genomic regions (top right panel). HBV, deficient for the expression of transcriptional regulator HBx (HBV x-), is transcriptionally repressed and is associated with SMC5/6 complex and interacts preferentially with heterochromatin and compartment B genomic regions (top left panel). A zoomed version of HBV wild-type infection (middle panel) highlights the preferential contacts of cccDNA with CpG islands enriched for Cfp1, transcription start sites (TSS) and enhancers. HBV cccDNA is associated with chromosome 19 and contacts an active enhancer. This spatial association is mediated by YY1 and HBx. Lower panel: the non-random location of HBV and association with euchromatin provides a favorable environment for HBV transcription. HBV contacts in turn interfere with cellular gene regulation and can lead to up or downregulation of host genes.