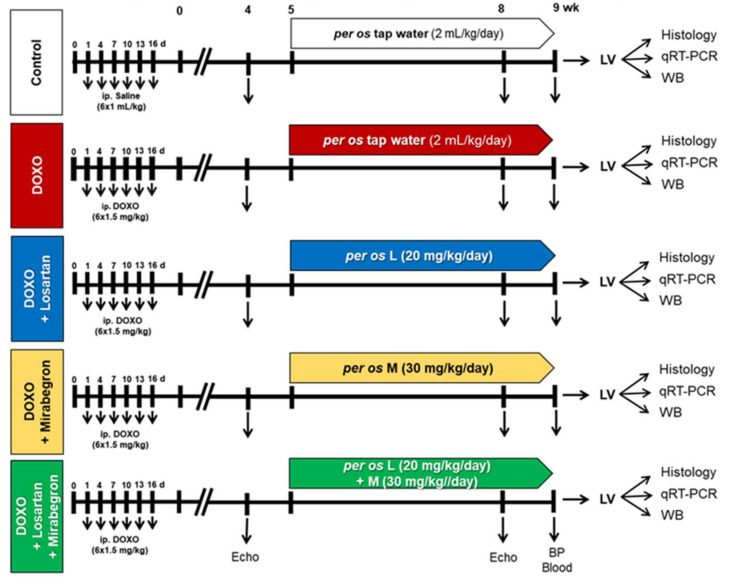
Figure 1.
Experimental protocol. Male Wistar rats (n = 50, 350–400 g) were divided into one control and four doxorubicin (DOXO)-treated groups (ip. 1.5 mg/kg in 6 cycles; cumulative dose: 9 mg/kg). From the 5th week after the last cycle of DOXO administration, rats were treated via oral gavage daily until the end of the experiments as follows: (i) control group treated with tap water (n = 8, 2 mL/kg/day), (ii) DOXO-only group treated with tap water (n = 11, 2 mL/kg/day), (iii) DOXO group treated with losartan (L, per os 20 mg/kg/day, n = 10) dissolved in tap water, iv) DOXO group treated with mirabegron (M, per os 30 mg/kg/day, n = 10) dissolved in tap water, and (v) DOXO group treated with the combination of losartan (per os 20 mg/kg/day) and mirabegron (per os 30 mg/kg/day) dissolved in tap water (n = 11, 2 mL/kg/day). Cardiac morphology and function were assessed by transthoracic echocardiography (Echo) at weeks 4 and 8 under isoflurane anesthesia. At week 9, an invasive blood pressure (BP) measurement was performed under pentobarbital anesthesia, then blood was collected from the abdominal aorta to measure routine laboratory parameters, and hearts, lungs, and tibias were isolated. Left and right ventricles were separated, and left ventricular samples were prepared for histology, qRT-PCR, and Western blot (WB) measurements.