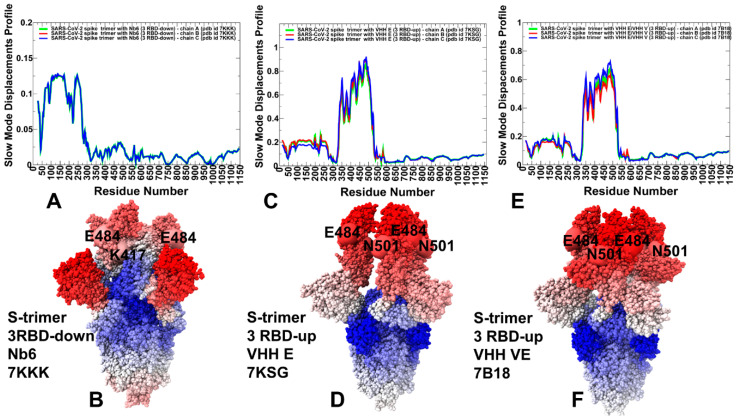
Figure 4.
The slow mode displacement profiles of the SARS-CoV-2 S trimer structures. The low-frequency essential mobility profiles are averaged over the first three major low-frequency modes. The essential mobility profiles of the SARS-CoV-2 S trimer in the complex with Nb6 nanobody, pdb id 7KKK (A), S trimer in the complex with VHH E nanobody, pdb id 7KSG (C), and S trimer in the complex with VHH E/VHH V nanobody, pdb id 7B18 (E). Structural maps of the slow mode profiles for the SARS-CoV-2 S trimer in the complex with Nb6 nanobody (B), S trimer in the complex with VHH E nanobody, (D), and S trimer in the complex with VHH E/VHH V nanobody (F). The structures are in sphere-based representation rendered using UCSF ChimeraX [108] with the rigidity-to-flexibility sliding scale colored from blue to red. The positions of sites of circulating mutations K417, E484, and N501 are shown in large spheres and highlighted for the protomers. The structural maps are projected onto the original cryo-EM structures.