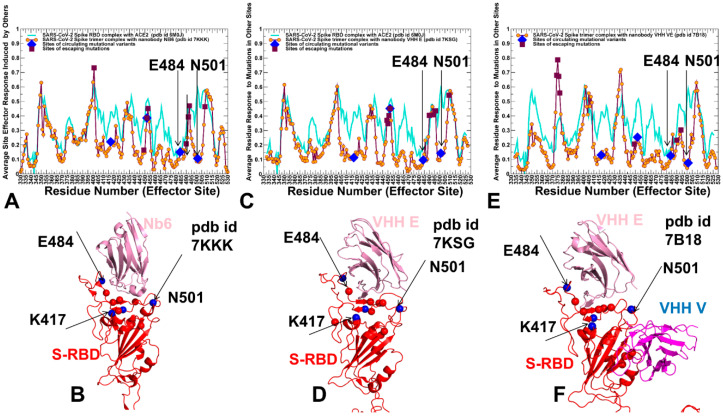
Figure 8.
The PRS effector profiles for the SARS-CoV-2 S trimer complexes with Nb6 nanobody, pdb id 7KKK (A), VHH E nanobody, pdb id 7KSG (C), and VHH VE nanobody, pdb id 7B18 (E). The PRS effector profiles for the SARS-CoV-2 S complexes are shown in maroon-colored lines with orange-colored filled circles. For comparison, the PRS profiles are superimposed with the respective profiles for the S-RBD complex with ACE2 shown in cyan-colored lines (pdb id 6M0J). The sites of escaping mutations for nanobody binding are indicated by maroon-colored filled squares, and RBD sites K417, E484, and N501 targeted by global circulating variants are highlighted in blue-colored filled diamonds. The positions of sites of circulating variants E484 and N501 are indicated by arrows on panels (A,C,E). These sites are aligned with the local minima of the PRS profile and may act as receivers/transmitters of the allosteric signal involved in functional RBD movements. Structural maps of the allosteric effector hotspots corresponding to the local maxima of the PRS profile are shown for the SARS-CoV-2 S trimer complex with Nb6 nanobody (B), S trimer complex with VHH E nanobody (D), and S trimer complex with VHH E/VHH V nanobody (F). The S-RBDs are shown in red-colored ribbons rendered using UCSF ChimeraX [108]. Structural positions of allosteric effector centers are shown in red spheres. The important functional sites subjected to circulating mutations K417, E484 and N501 are shown in blue spheres. The bound nanobodies Nb6 (B) and VHH E (D) are shown in pink-colored ribbons. VHH E/VHH V nanobody is shown in pink and magenta-colored ribbons, respectively (F).