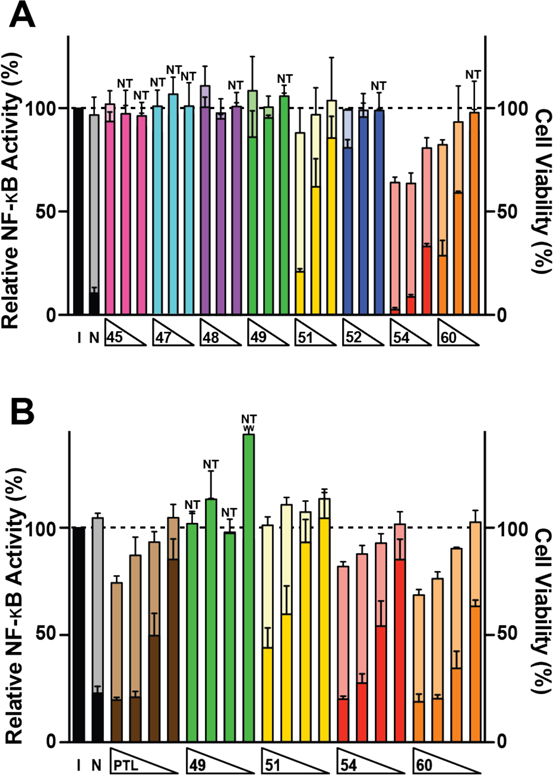
Figure 4.
Modulation of canonical NF-κB signaling by α-methylene-γ-lactams. (A) Compounds were tested at 20, 10, and 5 μM and NF-κB signaling was induced with TNF-a (15 ng/mL) in A549 cells containing a NF-κB driven luciferase gene. (B) Compounds were tested at 7.5, 5.0, 2.5, and 1.0 μM and NF-κB signaling was induced with TNF-a (22.5 ng/mL) in HEK293 cells containing a NF-κB driven secreted alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) gene. All wells in both assays were induced with TNF-α except for non-induced (N) control wells. Relative NF-κB activities (referenced to the induced, I, control set to 100%) are shown in dark colors. Accompanying cellular cytotoxicity measurements were made using Alamar Blue viability dye and are shown behind NF-κB inhibition in light colors. Cytotoxicity was normalized to the induced control, which was set at 100%. Columns marked with NT (non-toxic) indicate instances in which NF-κB activity (dark bars) obstructs the cellular cytotoxicity (light bars). Occluded values range from 88–101% (Table S1). Values shown are mean ± S.D. for n ≥ 3 biological replicates. PTL = parthenolide. See SI Tables S1 and S2 for numerical values.