FIGURE 7.
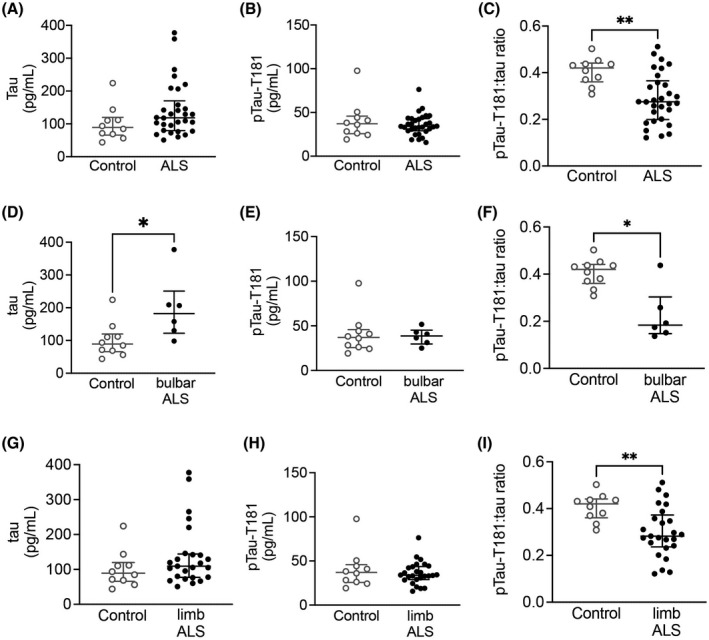
CSF pTau‐T181:tau ratio is decreased in ALS. While there was no difference in CSF (A) tau (Mann–Whitney U test = 100, p = 0.1234) and (B) pTau‐T181 (Mann–Whitney U test = 147, p = 0.8227), there was a significant decrease in (C) pTau‐T181:tau ratio (Mann–Whitney U test = 56, p = 0.0025) in ALS CSF (n = 40) compared with healthy controls (n = 10). (D) There was a significant increase in CSF tau levels in bulbar onset ALS (n = 6) (Mann–Whitney U test = 9, p = 0.0225). (E) CSF pTau‐T181 levels were not altered in bulbar onset ALS (Mann–Whitney U test = 27, p = 0.7925). (F) CSF pTau‐T181:tau ratio was significantly decreased in bulbar onset ALS (Mann–Whitney U test = 7, p = 0.0110). (G) CSF tau (Mann–Whitney U test = 91, p = 0.2253) and (H) pTau‐T181 levels (Mann–Whitney U test = 123, p = 0.8214) were not altered in limb onset ALS (n = 25). (I) There was a significant decrease in pTau‐T181:tau ratio in limb onset ALS (Mann–Whitney U test = 49, p = 0.0045). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01
