Figure 2.
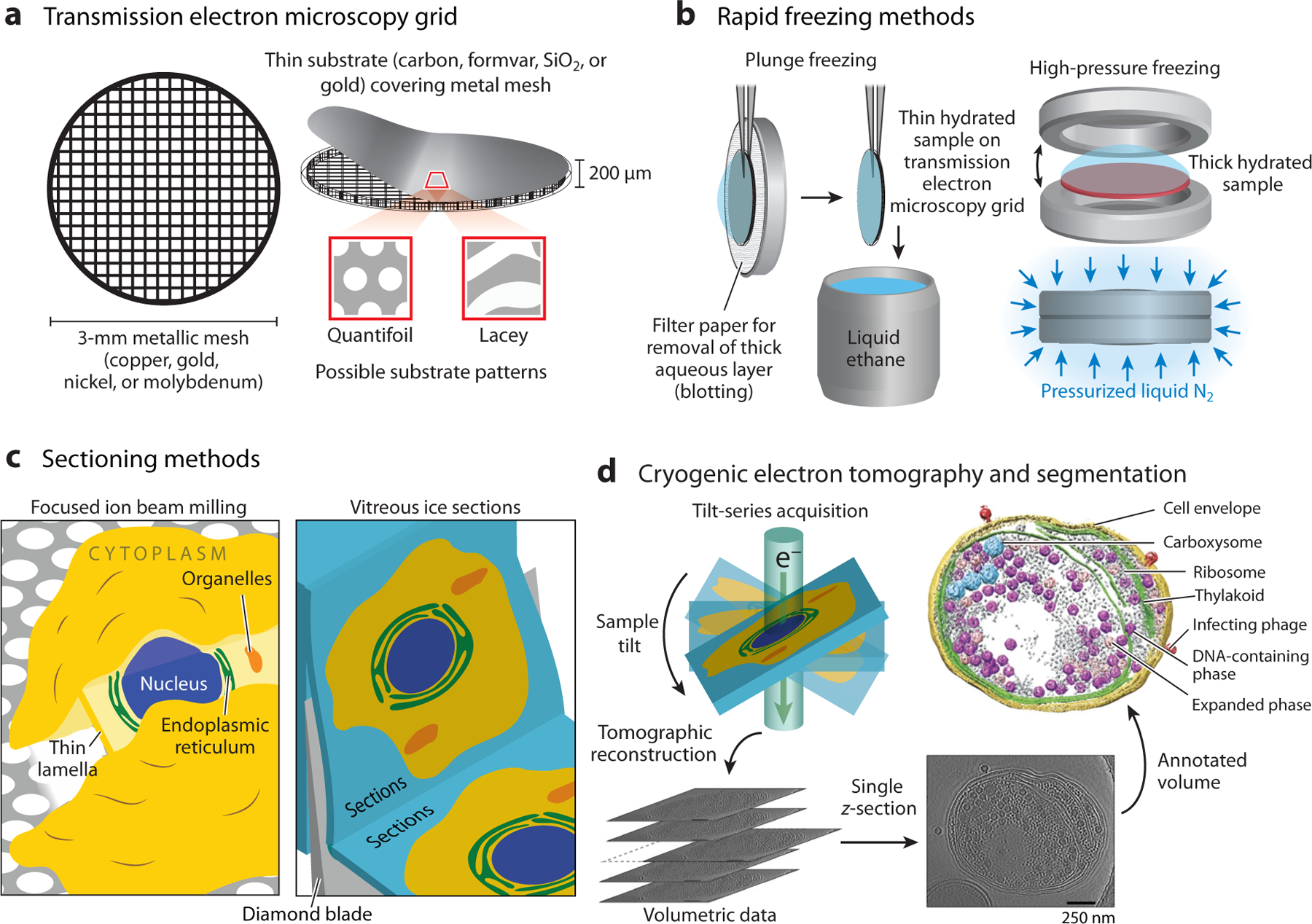
Cryogenic electron tomography (CET) sample preparation and data collection methods. (a) Transmission electron microscopy grids for cryogenic electron microscopy consist of a metallic mesh covered with a thin substrate layer. (b) Plunge freezing and high-pressure freezing are the most common methods used to rapidly freeze the sample. These methods preserve the sample in its native hydrated state encased in amorphous ice. (c) Thick samples cannot be directly analyzed due to the limited penetration of the electron beam. (Left) Focused ion beam milling uses a beam of gallium ions to ablate the sample to produce a thin lamella. (Right) Vitreous ice sectioning uses a diamond blade to cut serial thin sections. (d) CET data consists of multiple projections of the sample acquired by rotating the sample relative to the transmitted electron beam. These projections are then computationally reconstructed to produce a 3D volume that can be annotated to visualize features of interest. Data in panel d adapted with permission from Reference 151; copyright 2014 Springer Nature.
