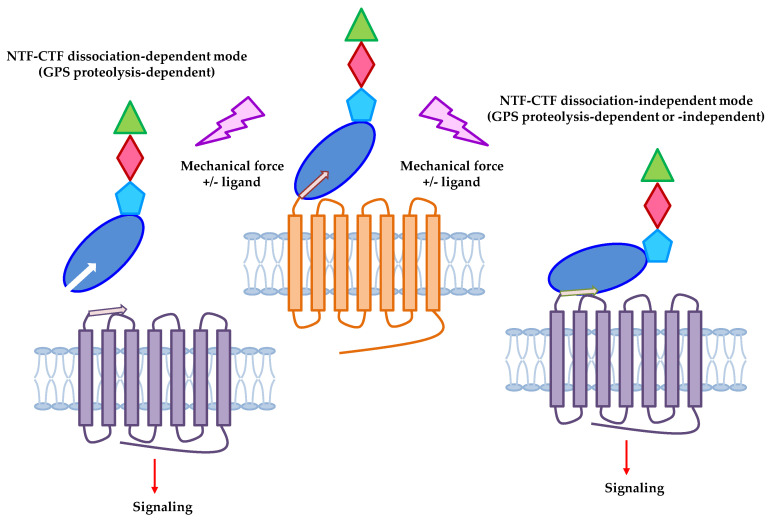
Figure 2.
Potential activation mechanisms of mechanosensitive aGPCRs. Mechanosensitive aGPCRs might be activated by mechanical stimulation in the absence or presence of specific ligands via the NTF-CTF dissociation-dependent (left) or NTF-CTF dissociation-independent (right) mechanism [8]. In the dissociation-dependent mechanism, GPS proteolysis of aGPCRs and NTF shedding are absolutely required for the exposure of the Stachel peptide and the activation of CTF. In contrast, aGPCRs can be activated via a GPS proteolysis-dependent or -independent manner in the dissociation-independent mechanism. In this model, the Stachel peptide is partially exposed and bound to the 7TM region due to conformational changes of ECR induced by ligand/mechanical stimuli.