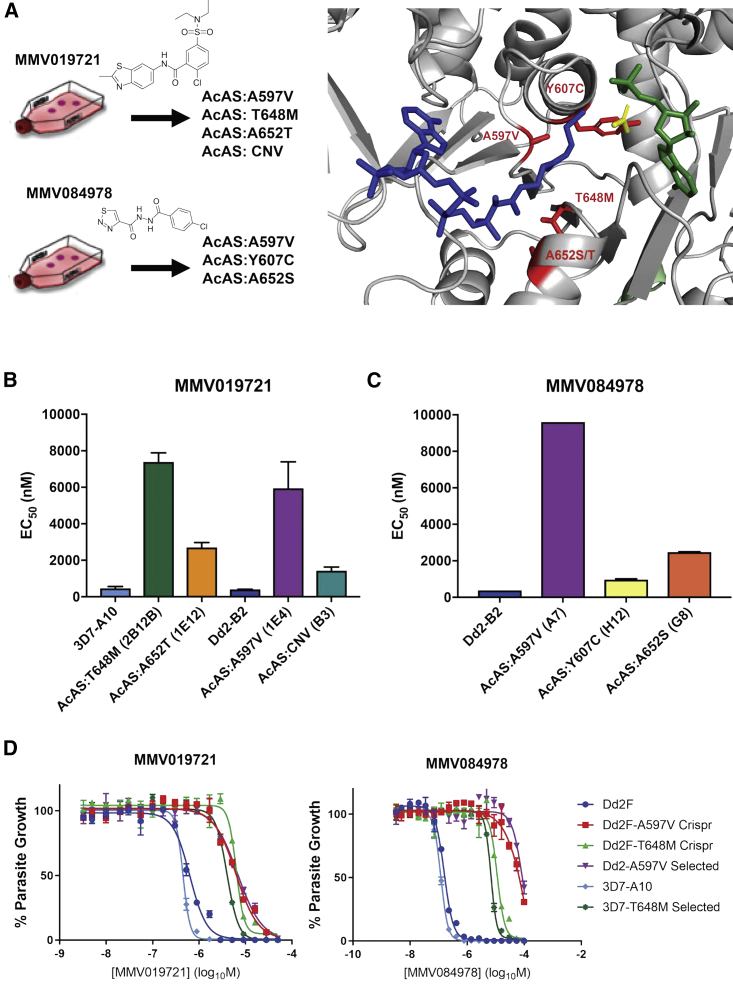
Figure 1.
Mutations in the P. falciparum acetyl-CoA synthetase (PfAcAS) confer resistance to MMV019721 and MMV084978
(A) Homology modeling of PfAcAS reveal that mutations identified in parasites resistant to MMV019721 or MMV084978 line the predicted active site of the enzyme.
(B and C) The in vitro susceptibility of representative drug-resistant cloned parasite lines identified as carrying mutations in PfAcAS by WGS. Data represent the mean + standard deviation (SD) of four experiments conducted in triplicate for MMV019721, and the mean + SD of two experiments conducted in triplicate for MMV084978.
(D) Representative dose-response assays for the 3D7 (light blue) and Dd2 (dark blue) parent lines, resistance-selected clones carrying A597V (purple) or T648M (light green), and CRISPR-Cas9 gene-edited parasites bearing A597V (red) or T648M (dark green). Shown is one representative biological replicate experiment run with technical triplicates.
See also Figures S1 and S2, and Tables S1, S2, and S3.