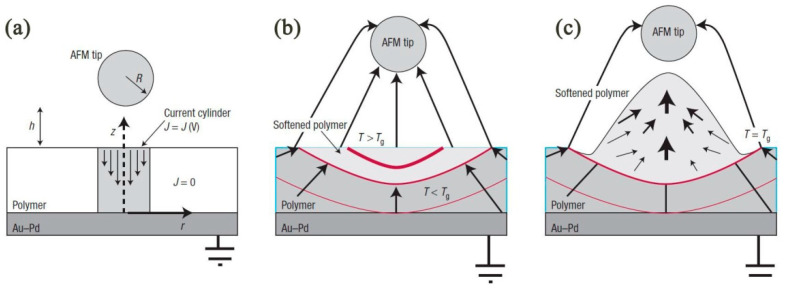
Figure 20.
(a) Geometrical arrangement of AFM and polymer. Initial tip–surface distance is typically 1–5 nm. In general, the specific spatial details of the tip–surface contact profile, as well as cantilever deformation, with applied bias during writing is not well understood or documented. To a zero-order approximation, the geometrical details arising from the relative orientation of the AFM pyramidal tip with respect to the surface is ignored, and the AFM tip is approximated as a sphere of radius ~35 nm. J = J (V) is the current density, which is a function of the applied (bias) voltage. (b) Joule heating from amplified current flow increases temperature within the polymer film (isotherms (red solid lines) determined from time-dependent heat-transfer calculations). T > Tg defines the volume of softened viscoelastic polymer. The highly non-uniform electric field (109–1010 V m−1, estimated by method of images) generates a step electric field gradient (arrows). (c) The large non-uniform electric field gradient that surrounds the AFM tip produces an electrostatic pressure on the polarizable, softened polymer creating raised features. The schematics of the mechanism of B-SPL. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [114]. Copyright 2022 Springer Nature.