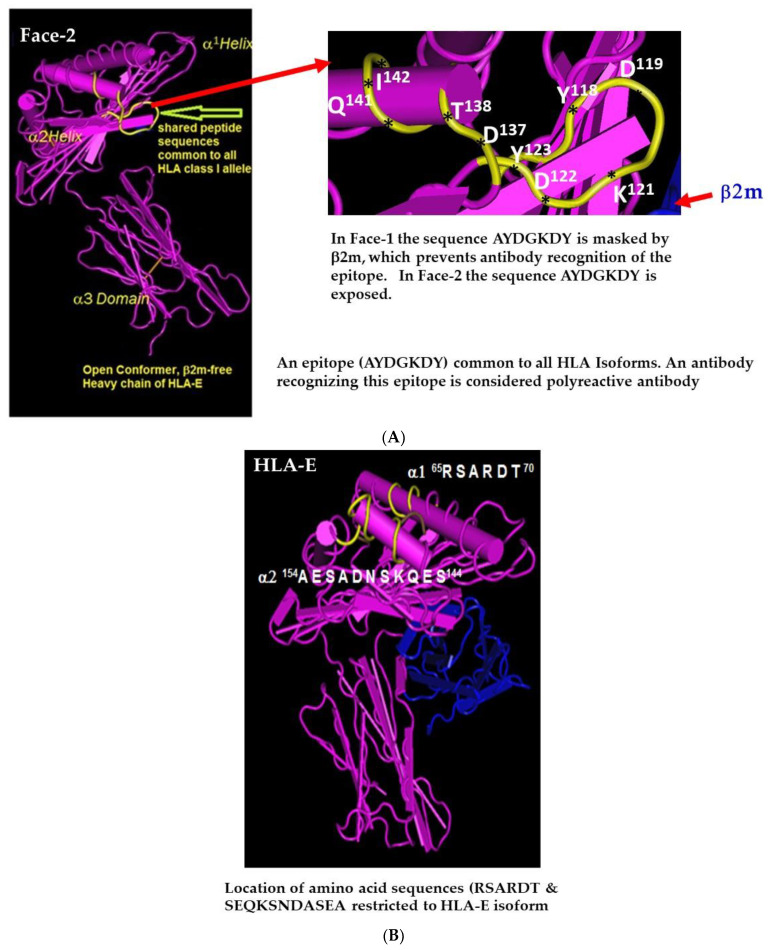
Figure 4.
(A) Exposed cryptic peptide sequences of an HLA-I devoid of β2 in Face-2. Sequence (117AYDGKDY123) is the most commonly shared with other HLA alleles of five major isoforms is indicated in yellow (see also Table 2). An antibody binding to such an epitope shared by other HLA isoforms are called polyreactive antibodies. (B) Face-1 of HLA-E. HLA-I monospecific antibodies (mAbs) recognize epitopes exposed on α1 or α2 helix of an allele of an isoform. Monospecificity of a mAb (TFL-033) is illustrated with HLA-E restricted amino acid sequence RSARDT. This sequence is not shared with any other HLA isoforms. Dosimetric inhibition of the antibody binding to HLA-E with the specific sequence confirms the monospecificity of the mAb. Only monospecific mAbs are reliable for immunodiagnosis of HLA antigens expressed on human normal and cancer cells. A donor specific antibody is expected to be monospecific for the donor allele and not polyreactive with a sequence exposed on Face-2.