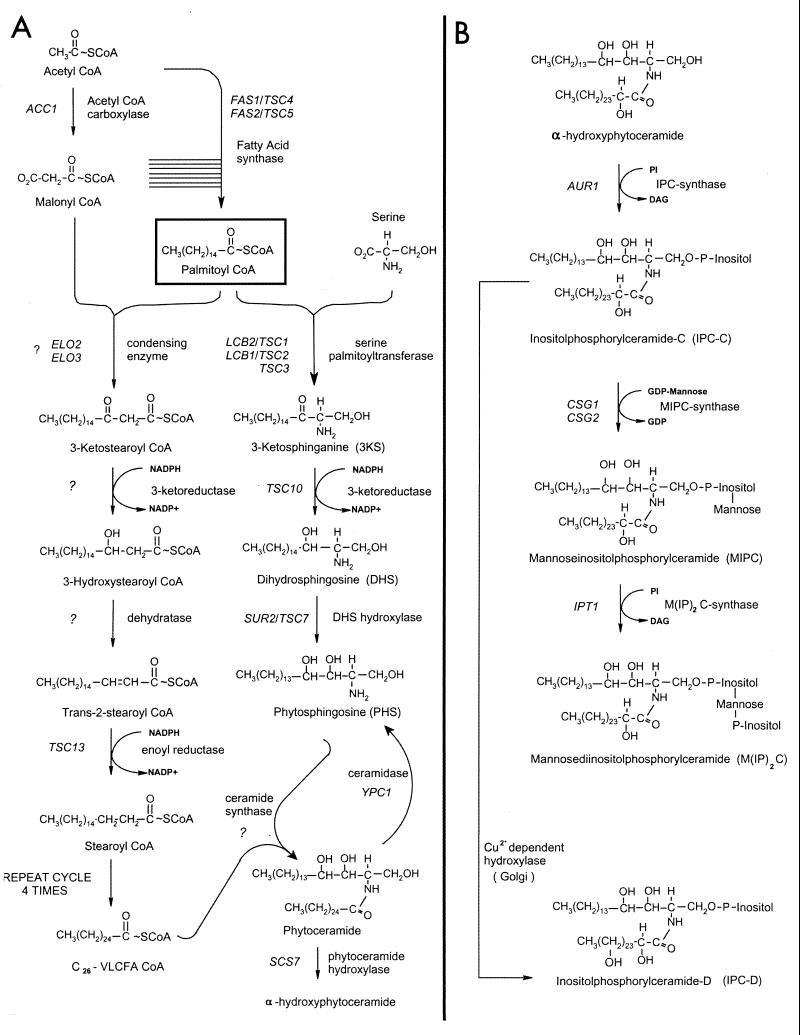
FIG. 1.
Pathways of fatty acid elongation, LCB, and sphingolipid synthesis in S. cerevisiae. Palmitoyl-CoA is synthesized from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA by soluble FAS. Palmitoyl-CoA is elongated to a C26 VLCFA by a membrane-associated fatty acid elongating system (A, left branch). Each cycle of elongation requires four successive reactions and lengthens the growing fatty acid by two carbon units; condensation of malonyl-CoA with the acyl-CoA substrate, reduction of the 3-ketoacyl-CoA, dehydration of the 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA, and reduction of the trans-2,3-acyl-CoA. Although the intermediates and the product of the elongation cycle are shown as CoA derivatives, this has not yet been experimentally confirmed. The organization of the elongating enzymes with respect to each other is unknown. The LCBs are synthesized by the pathway shown in the right branch of panel A; the pathway for the conversion of ceramide to mature sphingolipids is shown in panel B.