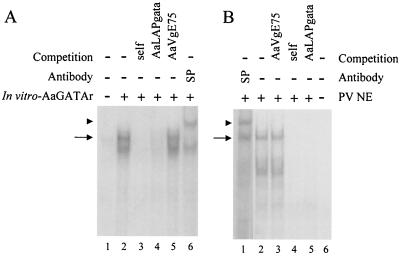
FIG. 6.
AaGATAr protein binds to a GATA binding site, and identification is performed for a functional GATA protein in fat body nuclear extracts of previtellogenic fat bodies. −, absence of substance; +, presence of substance. (A) EMSA using in vitro-transcribed and -translated AaGATAr and 32P-labeled Drosophila box A element as a probe. The GATA-specific complex is indicated by an arrow (lane 2). Fiftyfold molar excesses of cold probe (lane 3) or the AaLAP GATA binding site (lane 4) were included as specific competitors. The same excess of cold double-stranded oligonucleotide of an unrelated sequence (AaVgE75 binding site) was included in lane 5. The DNA-AaGATAr complex was supershifted by a B. mori anti-GATA serum (lane 6). An arrowhead indicates the position of the supershifted complex. In vitro-expressed full-length AaGATAr showed a small product due to an internal initiation site of transcription. (B) Nuclear extracts from previtellogenic fat bodies were examined by EMSA with AaVgGATAb element as a probe. The GATA complex was also supershifted by a B. mori anti-GATA serum (lane 1). An arrowhead indicates the position of the supershifted complex. The GATA-specific complex is indicated by an arrow. For competition analysis of this complex, 50-fold molar excesses of cold probe (lane 4) or AaLAP GATA oligonucleotide (lane 5) were included as specific competitors. The same amount of cold double-stranded oligonucleotide of an unrelated sequence was included in lane 3.