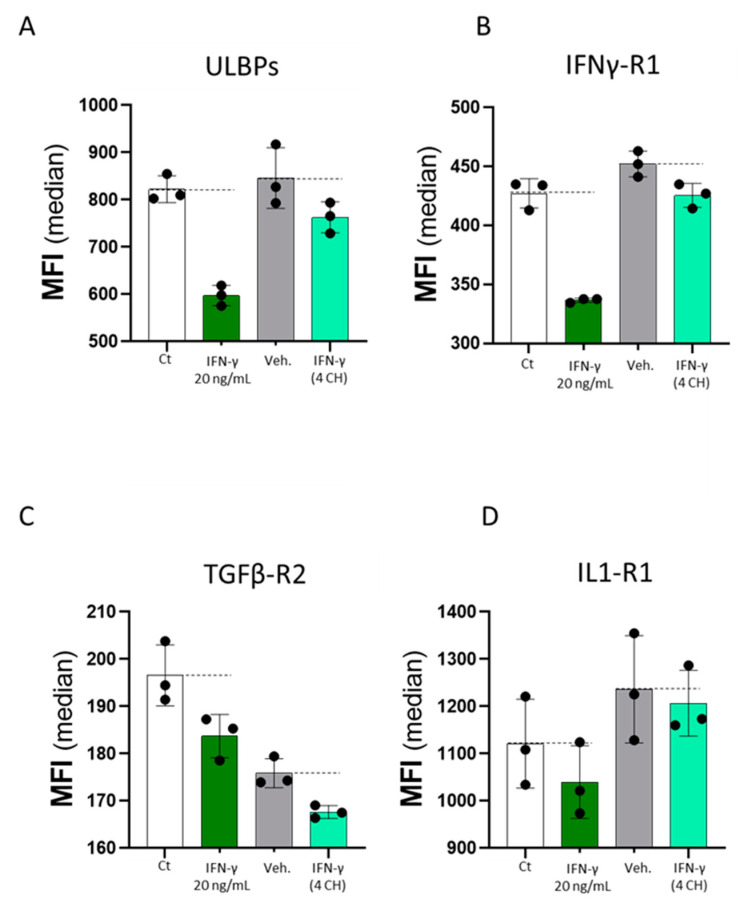
Figure 8.
Commercially available human recombinant IFN-γ (20 ng/mL) and homeopathically prepared IFN-γ (4 CH), each compared to their own controls, have both decreased the expression of the four tested immunity related endothelial cell surfaces. HUVECs were incubated during 48 h in the presence of IFN-γ (4 CH) or the vehicle (Veh.) The only medium was run as a negative control, while IFN-γ at 20 ng/mL was used as a positive control of the expected biological effects of IFN-γ. IFN-γ (20 ng/mL), as well as IFN-γ (4 CH), both decrease the expression of the four tested endothelial cell surface markers: ULBPs, IFNγ-R1, TGFβ-R2, and IL1-R1 (A–D). The results represent the mean ± SD of one technical triplicate for each condition. In order to well-read and interpret the graphs, we drawn two dotted lines per graph at the mean levels of either the medium control (Ct) or the Veh. control to observe and estimate the magnitude of effect induced by IFN-γ (20 ng/mL) or by IFN-γ (4 CH), respectively. In all the presented graphs, black dot lines were drawn to better visualize the effect of MIM compared to its Veh. control.