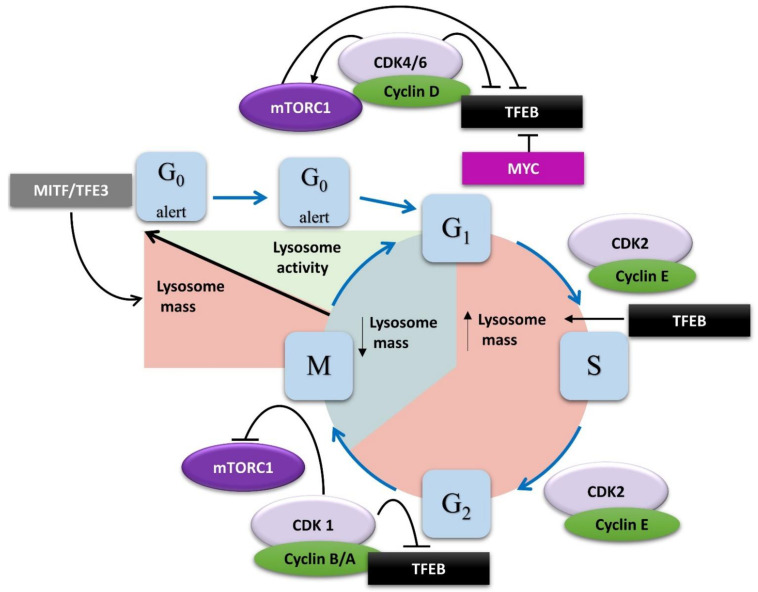
Figure 6.
Changes in lysosome mass and activity throughout the cell cycle. Lysosomal gene expression increases in deep quiescence as a result of elevated MITF and TFE3 activity. Priming from deep to shallow quiescence requires activation of lysosomal functions to promote catabolic pathways, providing energy required for cycling. As cells progress through G1 phase, CDK4/6 and MYC inactivate TFEB directly or via mTORC1 activation, decreasing lysosomal content. When cyclin D levels decrease in S phase, TFEB is released from the inhibitory effect of CDK4 and drives lysosomal gene expression, expanding the lysosomal compartment. During M phase, CDK1 inhibits TFEB and mTORC1, decoupling nutrients sensing from cell metabolism to protect genome integrity. As cells progress to anaphase, CDK1 is inactivated, and TFEB resumes lysosome biosynthesis, preparing cells for cytokinesis and mitotic exit.