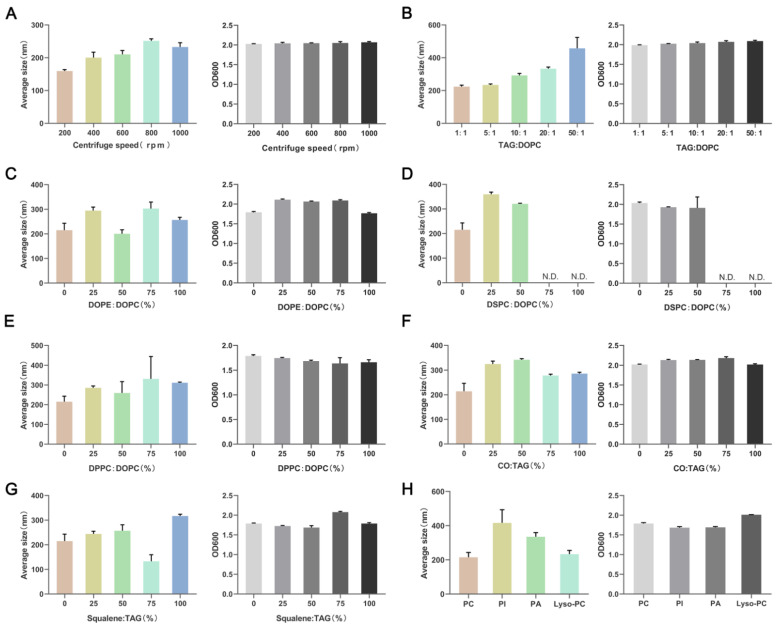
Figure 2.
Concentration (OD 600) and size (average size) of lipid nanoparticles prepared under different conditions. (A) Concentration (OD 600) and size (average size) of NLPs under different stirring speeds. (B) Concentration (OD 600) and size (average size) of NLPs generated with different ratios of DOPC and TAG. DOPC, 1,2-di(9Z-octadecenoyl)-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine; TAG, triacylglycerol. (C) Concentration (OD 600) and size (average size) of NLPs generated with different ratios of DOPE and DOPC. DOPE, 1,2-Dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine. (D) Concentration (OD 600) and size (average size) of NLPs generated with different ratios of DSPC and DOPC. DSPC, 1,2-Distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine. (E) Concentration (OD 600) and size (average size) of NLPs generated with different ratios of DPPC and DOPC. DPPC, 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine. (F) Concentration (OD 600) and size (average size) of NLPs generated with different ratios of CO and TAG. CO, Cholesterol. (G) Concentration (OD 600) and size (average size) of NLPs generated with different ratios of SQ and TAG. SQ, Squalene. (H) Concentration (OD 600) and size (average size) of NLPs generated with different ratios of multiple phospholipid fractions. The proportion of PI, PA and Lyso-PC to total phospholipids was 16.7%. PI, l-a-phosphatidylinositol; PA, phosphatidic acid; Lyso-PC, 1-hexanoyl-2-hydroxy-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine.