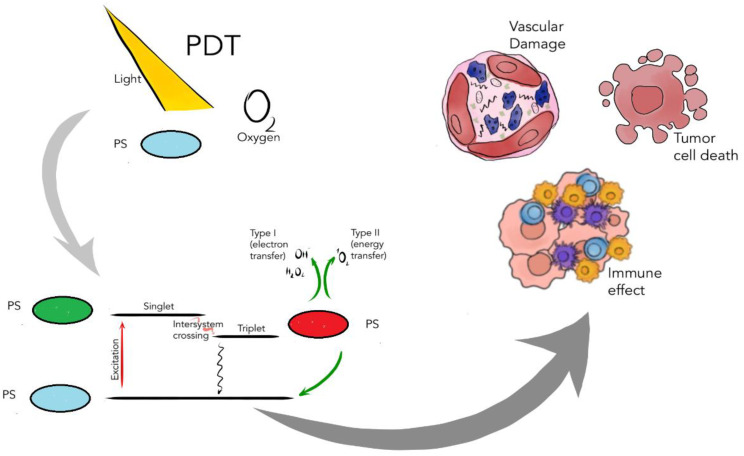
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of action of PDT such as inducing immune responses, damaging vascular structures and direct killing of tumor cells. PS’s generate ROS only after exposure to specific light and light activation in the presence of oxygen. Generated ROS mainly cause effector functions (e.g., killing cancer cells, inducing immune responses, damaging vascular structures and direct killing of tumor cells). Following light absorption, the PS reaches an excited singlet state. After an intersystem crossing, the PS, now in a triplet excited state, can react in two ways: react with biomolecules through a hydrogen atom (electron) transfer to form radicals, which react with molecular oxygen to generate ROS (Type I reaction), or the PS in its triplet state can react directly with oxygen through energy transfer, generating singlet oxygen (Type II reaction).