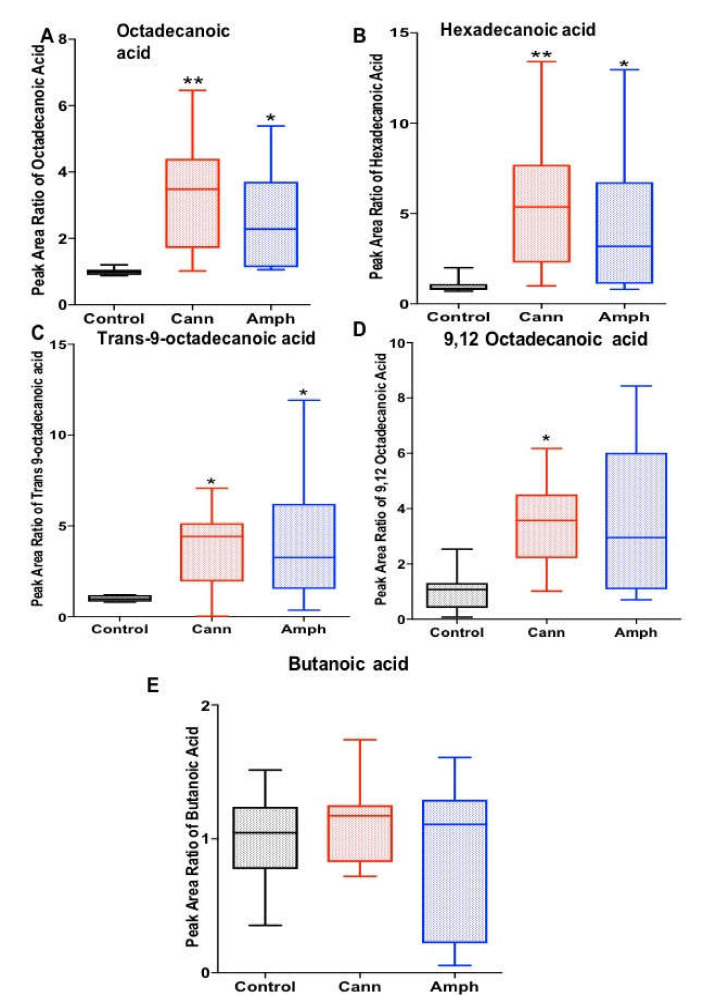
Figure 3.
Effects of cannabis or amphetamine on selected fatty acids in cannabis or amphetamine use disorder patients. (A) Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s post hoc analysis showed amphetamine and cannabis groups possessed higher octadecanoic acid compared with control group. (B) Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s post hoc analysis showed amphetamine and cannabis groups possessed higher hexadecenoic acid compared with control group. (C) Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s post hoc analysis showed that trans-9-octadecanoic acid was higher in the amphetamine or cannabis group compared with the control group. (D) Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s post hoc analysis revealed that 9,12 octadecanoic acid was higher in the cannabis group compared with the control group. (E) Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s post hoc analysis did not reveal significant changes in butanoic acid between the groups. (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01). Cann, cannabis. Amph, amphetamine.