FIG. 7.
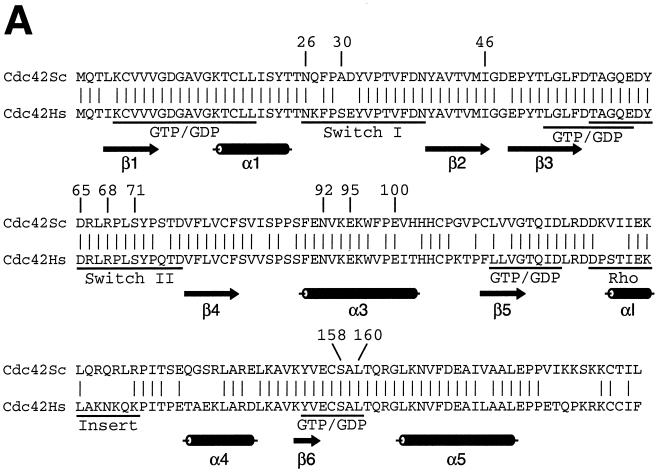
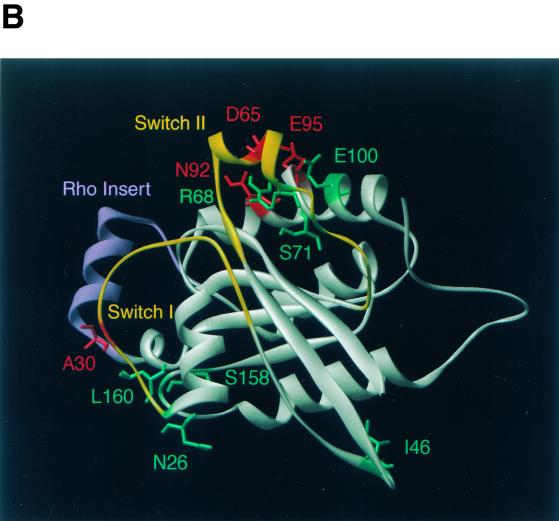
Cdc42p developmental mutations and structural model of Cdc42p. (A) Sequence alignment of Cdc42p from S. cerevisiae (Cdc42Sc) and from human (Cdc42Hs). Vertical lines indicate identical residues. Known GTP-binding/hydrolysis domains (GTP/GDP), switch I and switch II domains, and the Rho insert domain are underlined. Numbers indicate residues that were identified by mutations in the yeast Cdc42p sequence in this study. (B) Three-dimensional structure model of S. cerevisiae Cdc42p was obtained by homology modeling of the primary structure of S. cerevisiae Cdc42p using the Swiss-Model service (19) and is based on the X-ray crystal structure of Cdc42Hs (43, 53). Amino acid residues identified in this study are indicated in different colors based on the phenotypes caused by their exchange. Substitutions of green residues were found to suppress pseudohyphal or invasive growth, and exchanges of red residues enhanced pseudohyphal development. Switch I and switch II domains are colored yellow, and the Rho insert domain is shown in purple.