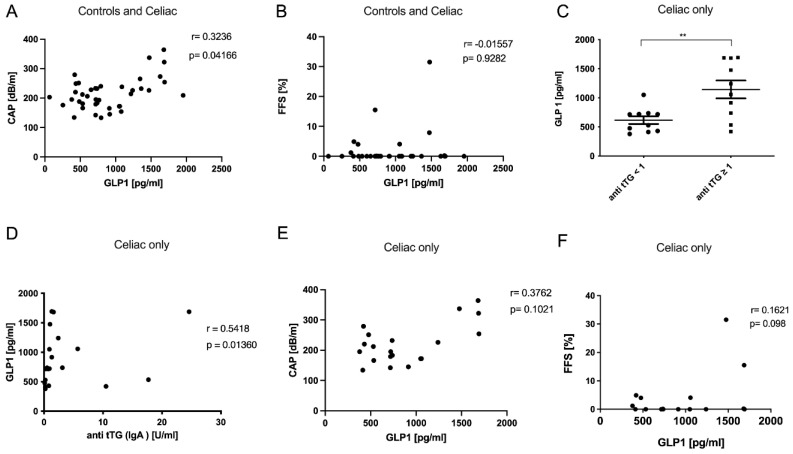
Figure 2.
GLP1 serum levels were associated with increased hepatic steatosis. The degree of steatosis as assessed by CAP (A) was associated with GLP1 in the entire study cohort, while this could not be confirmed by MRI (B). Celiac disease patients with increased anti-tTG antibodies had higher GLP1 serum concentrations (C), and these parameters also showed a positive correlation (D). Looking at the association of GLP1 with steatosis only in the celiac patients, we found the same trend by both CAP (E) and MRI measurements (F). ** p < 0.01.