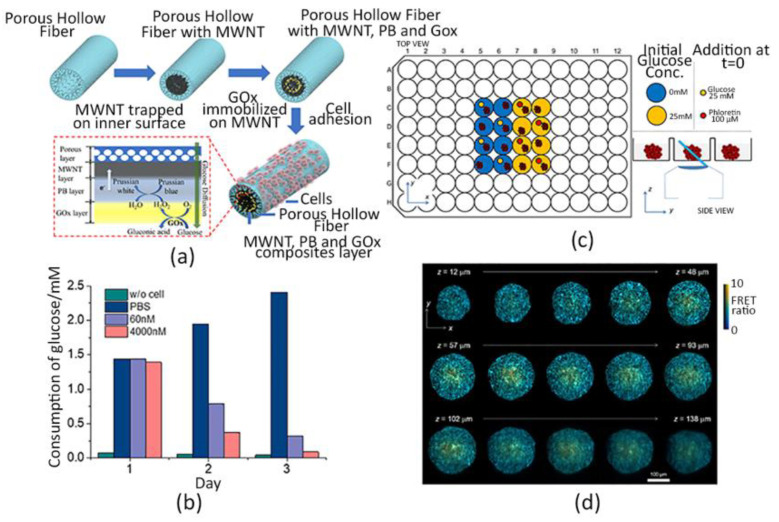
Figure 2.
Glucose monitoring. (a) Schematic representation of the cellularized PHF scaffold integrated with the enzyme-based glucose sensor. Human lung cancer cells (PC9) adhere on the outer wall of the structure working as a permeable barrier for the glucose diffusion, whereas the enzyme is immobilized in the lumen. Here, electrochemical reactions occur through the sensing system composed of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWNT), glucose oxidases (Gox) and Prussian blue (PB). (b) Glucose consumption per day by PC9 cells cultured over the PHF upon different Osimertinib concentrations. (c) Scheme of the experimental set up: Matrigel-based HEK293T cells spheroids expressing the glucose FRET biosensor gene were seeded in a 96-well plate; different experimental conditions were tested and observed with the OPM technique, which is capable of orienting the light sheet towards the samples [130]. (d) Spatial glucose distribution within the Matrigel-coated spheroids at different depths (z-axis). Color scale and brightness determine the expressed FRET ratio and the emission intensity, respectively [130]. (a,b) Adapted and reprinted from [123], Copyright (2020), with permission from Elsevier.