Figure 5.
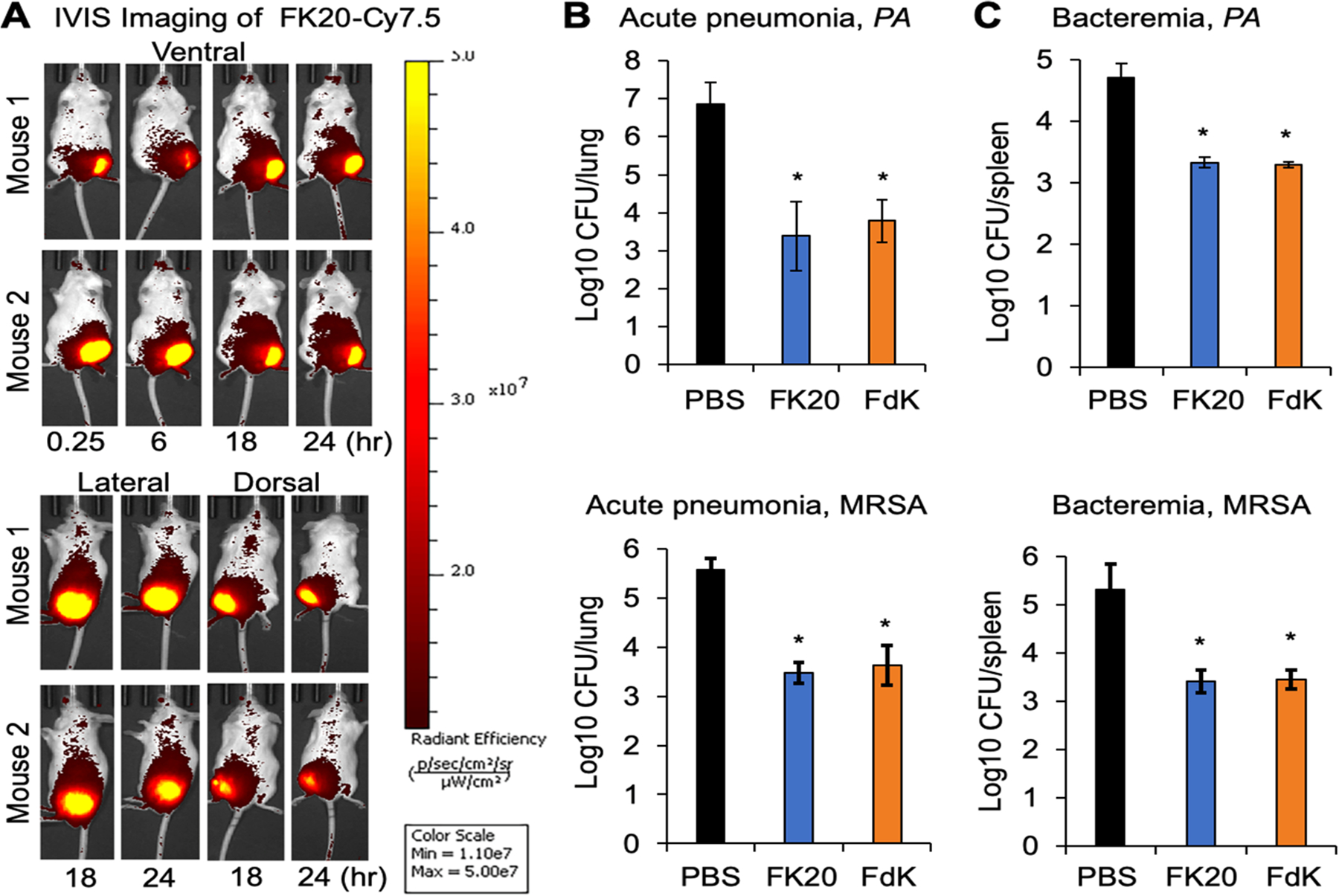
RPM efficacy in mouse models of pneumonia and bacteremia. (A) CD-1 mice (n = 2, males) were intramuscularly injected with FK20 conjugated to the fluorescence dye Cy7.5 (50 μg) in the left thigh and imaged in three positions over 24 h using an IVIS SpectrumCT imaging system. (B, C) CD-1 mice (7–9 week old, males and females) were inoculated with P. aeruginosa strain PAO1 or MRSA USA300 strain LAC. For the acute pneumonia model, mice were intranasally inoculated with 4.6 × 107 CFU of PAO1 for 24 h and 1.5 × 108 CFU of USA300 LAC for 48 h. For bacteremia, mice were intraperitoneally inoculated with 6.4 × 106 CFU of PAO1 and 7.6 × 106 CFU of USA300 LAC, and both models were followed for 24 h. Infected mice were treated intramuscularly twice daily with 5 mg/kg of FK20, FdK, or sterile PBS control. At the designated time, mouse lungs (acute pneumonia) or spleens (bacteremia) were harvested from euthanized mice, homogenized, and serially diluted and plated to determine bacterial burden. Error bars represent SD for n = 9 (pneumonia) or n = 6 (bacteremia). Significance was determined with the Student’s t test; *p < 0.05 significance compared to control.
