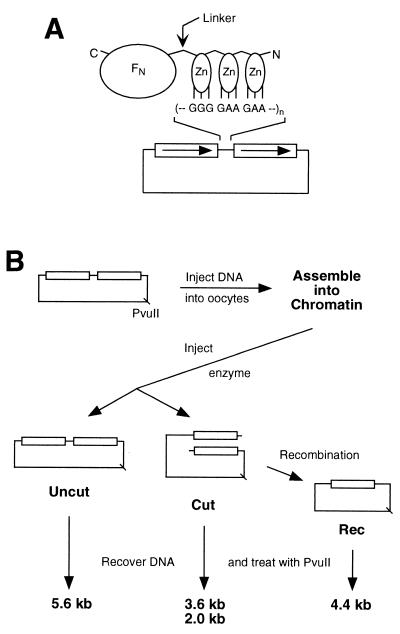
FIG. 1.
(A) Schematic diagram of a chimeric nuclease and DNA substrate. The nuclease consists of three zinc fingers (Zn) connected to the cleavage domain of FokI (FN) by a flexible peptide linker. The N and C termini of the protein are indicated. Each finger makes contact with three consecutive base pairs in the recognition sequence. In the DNA substrates, the canonical binding site for QQR, 5′-GGG GAA GAA, was inserted, in various numbers and orientations, between the 1.25-kb direct repeats (boxes with arrows) of plasmid pRW4. (B) Scheme for the oocyte injection experiments. The DNA substrate is diagrammed at the top left, and the position of the unique PvuII site is shown. For each sample the DNA was injected into the nuclei of 20 to 40 oocytes; they were incubated for 3 to 4 h to allow chromatin assembly, and then QQR was injected into the nuclei. After various lengths of time, DNA was recovered from the oocytes, digested with PvuII, and analyzed by Southern blot hybridization. This distinguishes DNA molecules not cleaved by QQR (Uncut) from cleaved DNA (Cut) and from cleaved molecules that have undergone homologous recombination (Rec). The locations of the PvuII sites and the sizes of the resulting PvuII fragments are shown.