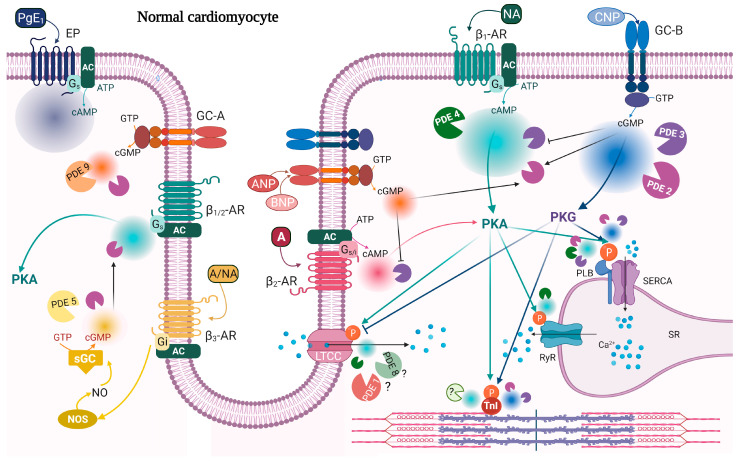
Figure 1.
cAMP/cGMP signaling and PDEs modulating contractility in normal cardiomyocytes. β1-AR stimulation causes a widespread rise in cAMP (cyan), which activates PKA phosphorylation of PLB, TnI, RyR, and LTCC. These events together lead to a positive inotropic response and a positive lusitropic response. Global and localized cAMP pools are under the control of PDE2 (purple), PDE3 (violet), and PDE4 (dark green) activity. β2-AR stimulation increases cAMP (pink), degraded by PDE2, and which affects contractility, but to a lower extent compared to β1-AR stimulation. CNP stimulation of GC-B gives a widespread increase in cGMP (blue) and PKG activation; PKG phosphorylates PLB and TnI and decreases LTCC current. These events contribute to a negative inotropic response and a positive lusitropic response. Global and local cGMP are degraded by PDE2 and PDE3. ANP stimulation of GC-A triggers a more restricted cGMP pool (orange) which does not seem to have a major direct role in contractility, and it is under the control of PDE2 and PDE9. cAMP/cGMP cross-talk is illustrated with black arrows indicating cGMP activation of PDE2 or inhibition of PDE3 activity towards cAMP. β3-AR stimulation can indirectly modulate contractility by increasing an NO-dependent cGMP pool which activates PDE2 and decreases β1/2-AR-stimulated contractility. This pool of cGMP (yellow) is degraded by PDE2 and PDE5. Prostanoid receptors (EP) stimulated by prostaglandin E1 (PgE1) increase cAMP with no effect on contractility. Shown also are receptors demonstrated to be present in T-tubule. Question marks indicate either unknown PDE or that the function of that PDE is not clear. A, adrenaline; AC, adenylyl cyclase; ANP, atrial natriuretic peptide; ATP/GTP, adenosine/guanosine triphosphate; BNP, brain natriuretic peptide; cAMP/cGMP, cyclic adenosine/guanosine 3′,5′-monophosphate; CNP, C-type natriuretic peptide; EP, prostanoid receptor; GC-A/B, guanylyl cyclase A/B; Gs/i, stimulatory/inhibitory G protein; LTCC, L-type calcium channel; NA, noradrenaline; NO, nitric oxide; NOS, nitric oxide synthases; p, indicates phosphorylation; PDE, phosphodiesterase; PgE1, prostaglandin E1; PKA/PKG, protein kinase A/G; RyR, ryanodine receptor; SERCA, sarcoendoplasmic reticulum (SR) calcium ATPase; sGC, soluble guanylyl cyclase; TnI, troponin I; β-AR, beta-adrenergic receptor. Created with BioRender.com, accessed on 7 February 2022.