FIG. 2.
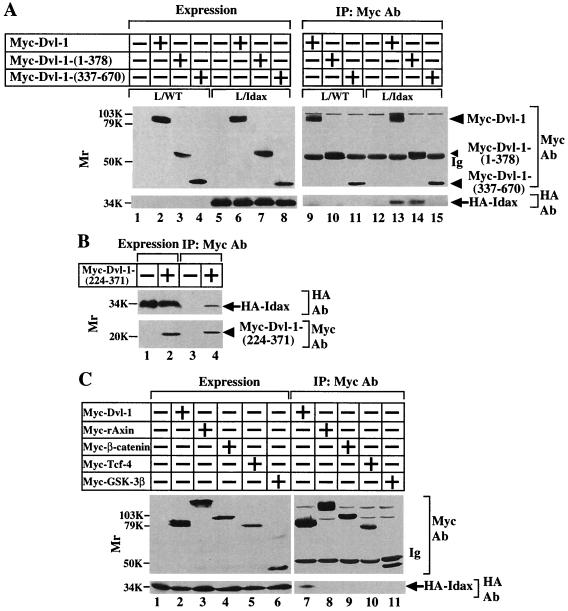
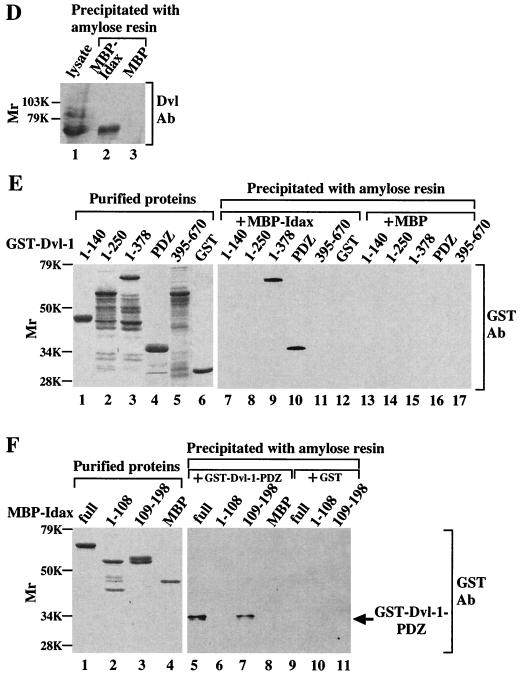
Interaction of Idax with Dvl. (A) Interaction of Idax with Dvl in intact cells. The lysates (20 μg of protein) of wild-type L cells (lanes 1 to 4) or L-Idax cells (lanes 5 to 8) expressing Myc–Dvl-1 (lanes 2 and 6), Myc–Dvl-1-(1-378) (lanes 3 and 7), or Myc–Dvl-1-(337-670) (lanes 4 and 8) were probed with the anti-Myc and anti-HA antibodies. The same lysates (150 μg of protein) prepared in lanes 2 to 8 were immunoprecipitated with the anti-Myc antibody, and the immunoprecipitates were probed with the anti-Myc and anti-HA antibodies (lanes 9 to 15). IP, immunoprecipitation; Ab, antibody. (B) Interaction of Idax with the PDZ domain of Dvl. The lysates of L-Idax cells with (lane 2) or without (lane 1) expression of Myc–Dvl-1-(224-371) were probed with the anti-Myc and anti-HA antibodies. The same lysates (150 μg of protein) prepared in lanes 1 and 2 were immunoprecipitated with the anti-Myc antibody, and the immunoprecipitates were probed with the anti-Myc and anti-HA antibodies (lanes 3 and 4). (C) Inability of Idax to bind to other Wnt signaling molecules. The lysates (20 μg of protein) of L-Idax cells expressing Myc–Dvl-1 (lane 2), Myc-rAxin (lane 3), Myc–β-catenin (lane 4), Myc–Tcf-4 (lane 5), or Myc–GSK-3β (lane 6) were probed with the anti-Myc and anti-HA antibodies. The same lysates (150 μg of protein) prepared in lanes 2 to 6 were immunoprecipitated with the anti-Myc antibody, and the immunoprecipitates were probed with the anti-Myc and anti-HA antibodies (lanes 7 to 11). (D) Complex formation of Idax with Dvl in rat brain. Rat brain cytosol (30 μg of protein) was probed with the anti-Dvl antibody (lane 1). The cytosol (100 μg of protein) was incubated with MBP-Idax (lane 2) or MBP (lane 3) (30 pmol) immobilized to amylose resin, and MBP fusion proteins were precipitated by centrifugation and the precipitates were probed with the anti-Dvl antibody. (E) Direct interaction of Idax with Dvl. GST–Dvl-1-(1-140), GST–Dvl-1-(1-250), GST–Dvl-1-(1-378), GST–Dvl-1-PDZ, GST–Dvl-1-(395-670), and GST (1 μg of protein) were stained with Coomassie brilliant blue (lanes 1 to 6). GST–Dvl-1-(1-140) (lanes 7 and 13), GST–Dvl-1-(1-250) (lanes 8 and 14), GST–Dvl-1-(1-378) (lanes 9 and 15), GST–Dvl-1-PDZ (lanes 10 and 16), GST–Dvl-1-(395-670) (lanes 11 and 17), or GST (lane 12) (1 μM) was incubated with MBP-Idax (lanes 7 to 12) or MBP (lanes 13 to 17) (30 pmol) immobilized on amylose resin, and MBP fusion proteins were precipitated by centrifugation and the precipitates were probed with the anti-GST antibody. (F) The region of Idax which binds to Dvl. MBP-Idax, MBP-Idax-(1-108), MBP-Idax-(109-198), and MBP (0.5 μg of protein) were stained with Coomassie brilliant blue (lanes 1 to 4). GST–Dvl-1-PDZ (lanes 5 to 8) or GST (lanes 9 to 11) (1 μM) was incubated with MBP-Idax (lanes 5 and 9), MBP-Idax-(1-108) (lanes 6 and 10), MBP-Idax-(109-198) (lanes 7 and 11), or MBP (lanes 8) (30 pmol) immobilized on amylose resin. MBP fusion proteins were precipitated by centrifugation, and the precipitates were probed with the anti-GST antibody. The results shown are representative of three independent experiments.