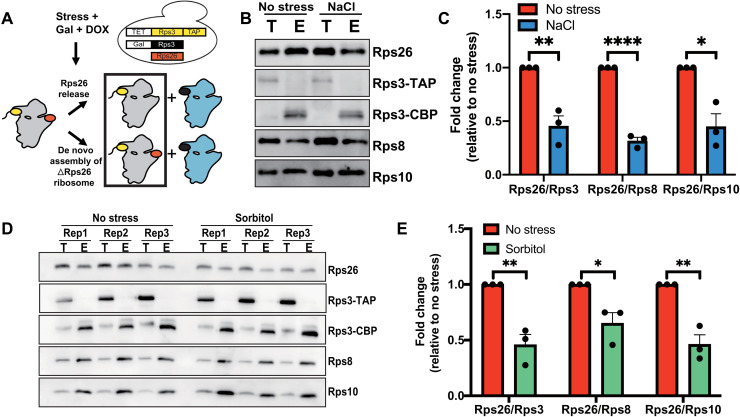
Fig. 1. Rps26-deficient ribosomes arise from preexisting 40S subunits.
(A) Pulse-chase experiments to separate preexisting ribosomes (gray) from newly made ribosomes (blue) rely on a yeast strain with Rps3-TAP produced from a TET-repressible promoter (yellow), and Rps3 (black) produced from a galactose-inducible/glucose-repressible promoter. Rps26 is shown in red. By shifting this strain from glucose to galactose/dox, preexisting ribosomes are marked with the Rps3-TAP affinity purification handle and will be in the TAP-elution, as indicated by the black box. (B) Western blot of preexisting (Rps3-TAP) ribosomes isolated by affinity purification from cells treated or not treated with 1 M NaCl before lysis. T, total lysate; E, elution. Note that elution from the IgG beads by TEV protease converts Rps3-TAP (Rps3–CBP–protein A) to Rps3-CBP (Rps3-calmodulin–binding protein). (C) Quantification of data in (B). Data are averaged from three biological replicates. Error bars represent the SEM, and significance was determined using an unpaired t test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001. (D) Western blot of preexisting (Rps3-TAP) ribosomes isolated by affinity purification from cells treated or not treated with 1 M sorbitol before lysis. (E) Quantification of data in (D). Data are averages from three biological replicates. Error bars represent the SEM, and significance was determined using an unpaired t test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.