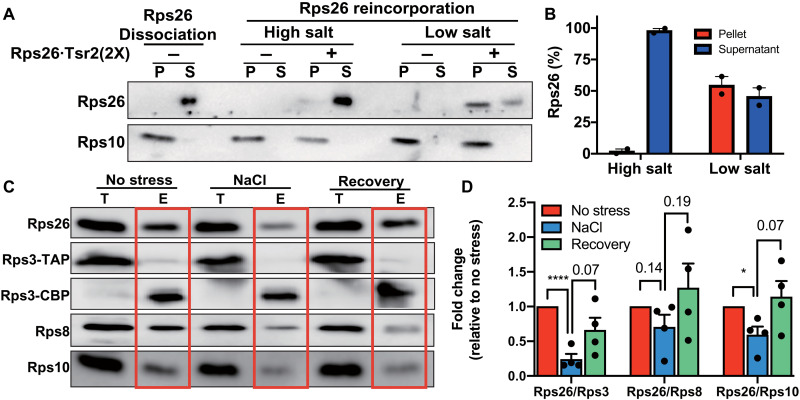
Fig. 4. Repair of Rps26-deficient ribosomes after stress.
(A) Rps26 cosedimentation with ribosomes after incubation of Rps26-deficient ribosomes with recombinant Rps26•Tsr2 in vitro. Western blot analysis of ultracentrifugation pelleting experiments. Rps26-deficient ribosomes (Rps26 dissociation) were generated by Tsr2 addition in 750 mM KOAc and separated from free Rps26•Tsr2 by ultracentrifugation. Rps26-deficient ribosomes were incubated with purified recombinant Rps26•Tsr2 in low (100 mM KOAc) or high (750 mM KOAc) salt buffers, and Rps26 binding was assessed after pelleting of the ribosomes. S, supernatant; P, pellet. (B) Data from two independent experiments were quantified. (C) Rps26 is reinserted into ribosomes in vivo. To monitor the repair of Rps26-deficient ribosomes by reinsertion of Rps26, the same pulse-chase experiment as in Fig. 1 was performed, except NaCl stress was relieved by dilution into fresh media. (D) Quantification of data in (C). Data are averages from four biological replicates. Error bars represent the SEM, and significance was determined using an unpaired t test. *P < 0.05; ****P < 0.0001.