Figure 6.
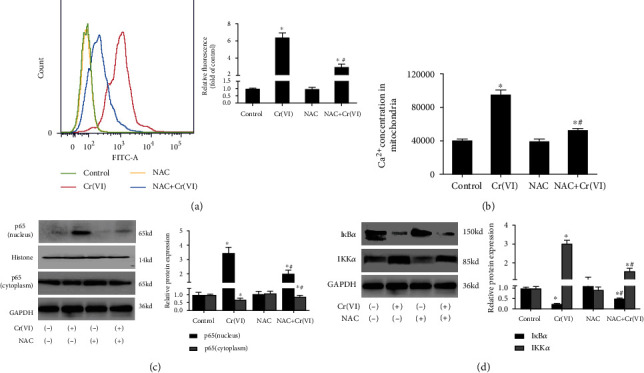
The intracellular Ca2+ overload and NF-κB activation caused by Cr(VI) depended on ROS accumulation. The L02 cells were pretreated with NAC for 1 h prior to Cr(VI) treatment for 4 weeks. (a) The intracellular Ca2+ concentration was assayed by flow cytometry (histogram) and spectrofluorometry (bar graph). (b) The fluorescence of mitochondria Ca2+ was quantitated via spectrofluorometry. (c) The protein levels of p65 (cytoplasm and nucleus) and (d) IκBα and IKKα were determined by Western blot. ImageJ software was used to analyze the relative levels of proteins normalized to the expression of GAPDH. All experiments were repeated at least 3 times and expressed as mean ± SD. ∗p < 0.05, compared with control; #p < 0.05, compared with Cr(VI)-exposed group. For the sake of clarity, the same control GAPDH was applied to compare with all experimentally relevant proteins with the same exposure time detected on the same SDS-PAGE gel unless otherwise stated.
