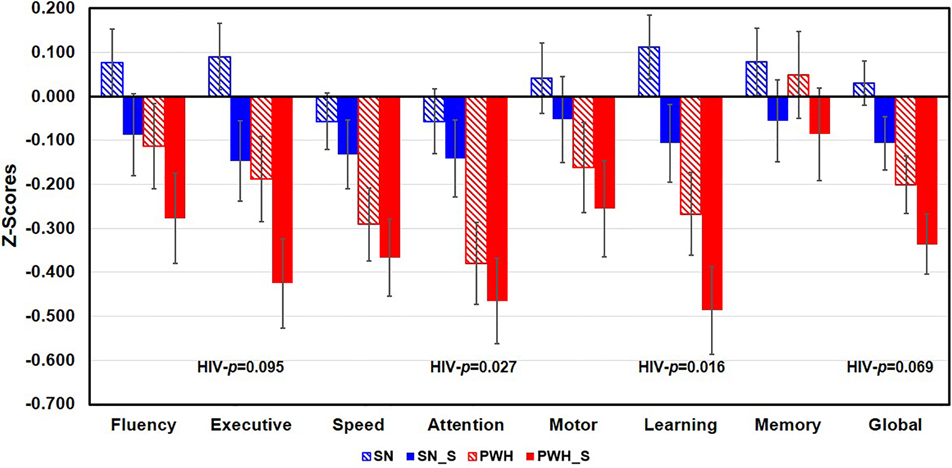
Figure 1. Cognitive Domain Z-Scores in the Four Participant Groups.
Regardless of smoking status, PWH participants had lower Z-scores in the Attention (p=0.027) and Learning (p=0.016) than SN participants. PWH participants also tended to have lower Z-scores on Executive function (p=0.095) and Global function (p=0.069) than SN participants. PWH=people with HIV disease and are non-smokers, SN= HIV seronegative non-smokers, SN_S=HIV seronegative tobacco smokers, PWH_S=PWH tobacco smokers. Subtests in each domain were listed below. Fluency: DKEFS Design Fluency and Verbal Fluency (with letters FAS); Executive Functions: DKEFS- Color-Word Interference Test Inhibition & Inhibition/Switching, DKEFS-Trail making Number-Letter Switching; Speed of Information Processing: Symbol Digit, DKEFS Trail-making Number Sequencing, DKEFS Color naming, and California Computerized Assessment Package (CalCAP) Simple Reaction Time; Attention/Working Memory: Arithmetic from Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-VI, Digit Span Backward, Letter-Number Sequencing, Arithmetic and Paced Auditory Serial Addition Test 1; Learning: Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test Trial 5 and Rey-Osterreith Complex Figure Test-Immediate Recall; Memory: Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test Delayed Recall (Trial 7) and Rey Complex Figure-Delayed Recall; Motor Skills, Grooved Pegboard Dominant and Non-dominant hands.