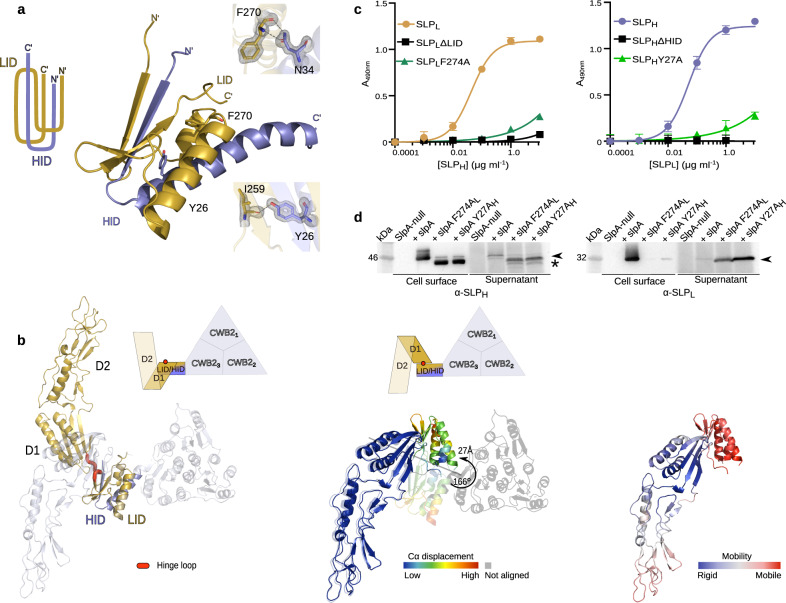
Fig. 2. Interactions and flexibility in C. difficile SLPH/SLPL (H/L) complex.
a Paperclip organisation of the interacting domains LID/HID is maintained by a range of interactions, with selected interface residues identified in strain R7404 (SLCT-7b, PDB ID: 7ACW) depicted as sticks. 2mFo-DFc electron density map is shown on the interacting amino acid pairs as a grey mesh contoured at 1.5 σ. Specific interatomic interactions identified with PDBePISA are represented as a dashed line. b Superimposing structures of SLPL/HID (gold/slate blue, PDB ID: 7ACV) onto the native complex of SlpAR7404 (SLCT-7b, PDB ID: 7ACX) (blue/white) reveals the flexibility of the LID-D1 linker, as illustrated by rotation of D1-D2 domains in relation to fixed position of LID/HID motif (left). The hinge loop enabling this conformational flexibility (determined by DynDom6D) is coloured in red. The backbone displacement (coloured from blue – low, to red – high Cα displacement deviation) is shown on the alignment of D1-D2 region of both structures (middle; SLPL/HID – opaque, H/L – semi-transparent) with the rotation angle of the LID/HID motif indicated with an arrow. Structural dynamics (right) of SLPL/HID, represented as increasing mobility (coloured blue – rigid, to red - mobile), calculated based on elastic network models implemented in DynOmics ENM version 1.0 server. c Probing of CD630 H/L complex interactions in vitro with ELISA, comparing effects of intact SLPL (gold circles), SLPH (slate blue circles), variants lacking interacting domains (black squares) and substitution mutants of F274A (structurally equivalent to F270 in R7404 LID/HID depicted in c, dark green triangles) and Y27A (structurally equivalent to Y26 in R7404 LID/HID in c, light green triangles) on H/L complex formation. Graphs represent mean ± standard deviation (SD) of n = 3 experiments, with least-squares curve fit of product formed upon the interaction of the two subunits. Source data provided in Source data file. d Western blot of cell surface extracts and culture supernatants, detecting (black arrowhead) SLPH (left) and SLPL (right) in strains devoid of endogenous slpA and expressing plasmid-borne SlpACD630 native protein or variants with either F274AL or Y27AH substitution mutants in SLPL or SLPH (denoted in subscript), respectively (n = 1). Detected product of partial degradation of SLPH indicated with an asterisk. Source data provided in Source Data file.