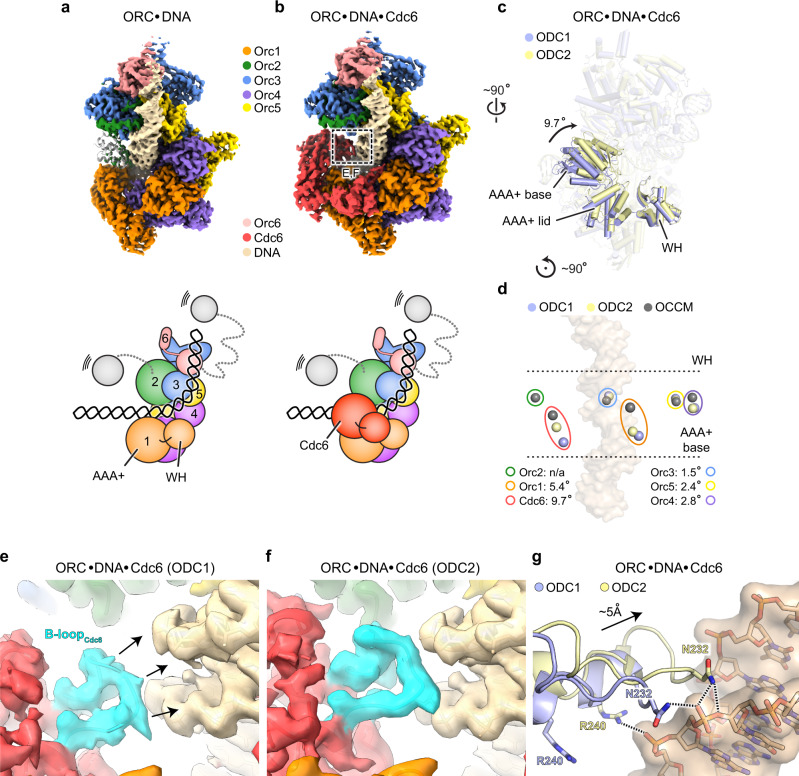
Fig. 1. Conformational changes in the ScORC·Cdc6 ring alter Cdc6’s DNA binding mode.
Cryo-EM structures of ARS1 DNA-bound ScORC (in a) and in complex with ScCdc6 (ODC1, in b). Unsharpened cryo-EM maps are shown surface-colored by subunit with schematics below. In a, the Orc2 WH domain of an ScORC·DNA structure obtained from crosslinked sample (PDB 5zr16) is shown as gray cartoon. Weak density in the current ScORC·DNA cryo-EM map indicates flexibility of this region in the uncrosslinked complex. Zoomed views of boxed region (in b) are provided in panels e and f. c Cdc6 is found in two different positions in the ORC·Cdc6 ring, which are related by a ~10° rotation of the subunit. Both ScORC·DNA·Cdc6 structures (ODC1 in blue and ODC2 in yellow) were aligned by superposing Orc2. Cdc6 is shown as solid cartoon while other subunits are transparent (WH – winged-helix domain). d Repositioning of Cdc6 is caused by movement of both Orc1 and Cdc6 in the ORC·Cdc6 ring. Centers of mass of the AAA+ base domains of Orc1-5 and Cdc6 in ODC1, ODC2, and OCCM (PDB 5v8f8) are shown as blue, yellow, and gray spheres, respectively. Corresponding subunits are outlined using colors as in (a). Angular displacements of corresponding subunits between ODC1 and ODC2 are listed. e–g Cdc6 repositioning facilitates novel contacts between the Cdc6-B-loop and DNA. Unsharpened cryo-EM map densities of DNA and the Cdc6 B-loops (highlighted in cyan) of ODC1 (in e) and ODC2 (in f) are shown. In g, the Cdc6 B-loop regions of ODC1 and ODC2 are superposed after structural alignment of the DNA duplexes. Electrostatic interactions are indicated by dashed lines. The color schemes used in this figure are maintained throughout the manuscript unless noted otherwise.