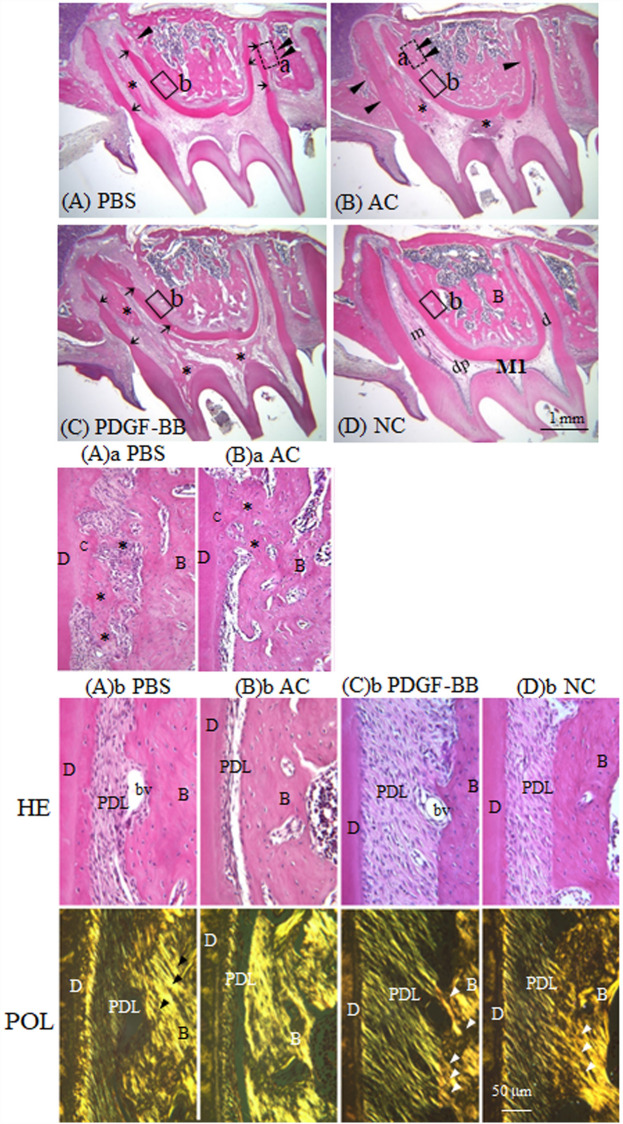
Figure 1.
(A–D) PDGF-BB effectively suppresses ankylosis and restores well-organized PDL structure after replantation. Haematoxylin and eosin staining of sagittal sections of replanted rat maxillary first molars in the four groups. (A) PBS-pretreated, (B) atelocollagen-pretreated (AC), (C) PDGF-BB-pretreated tooth (PDGF-BB) at 21 days. (D) A non-replanted normal tooth (NC). Arrowheads and arrows indicate bony attachments of root surfaces and root resorption lacunae, respectively. Black asterisks indicate bone-like structures in the dental pulp. m mesial root, d distal root. ((A)a, (B)a) Magnified views of ankylosed roots (dotted squares (a) in (A,B)) in sagittal sections of PBS- ((A)a) and AC- ((B)a) pretreated teeth 21 days after replantation. Asterisks indicate bone-like ankylotic tissues. ((A)b–(D)b) Magnified views of the periodontal ligament (solid squares (b) in (A–D)) in sagittal sections of PBS- ((A)b), AC- ((B)b) and PDGF- ((C)b) pretreated teeth 21 days after replantation, and a normal control tooth ((D)b). HE-stained images (HE, upper images) and images under polarized light (POL, lower images). Arrowheads indicate insertions of birefringent collagen fibre bundles into alveolar bones. B alveolar bone, C cementum, D dentine, bv blood vessel, PDL periodontal ligament.