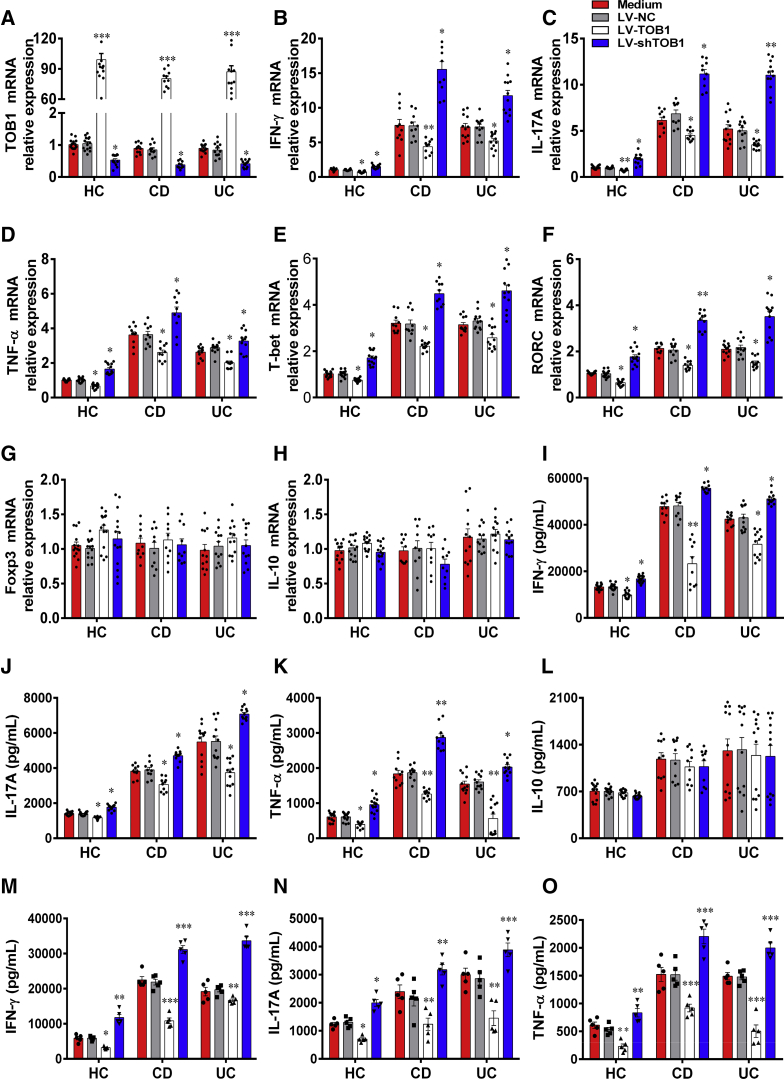
Figure 2.
Forced expression of TOB1 in IBD CD4+T cells restricts excessive Th1/Th17 cell immune responses. PB-CD4+ T cells from patients with A-CD (n = 10), patients with A-UC (n = 12), and HC subjects (n = 14) were transfected with LV-TOB1, LV-shTOB1, and LV-NC, respectively, and then cultured under stimulation with plate-bound anti-CD3 mAb (5 μg/mL) and soluble anti-CD28 mAb (2 μg/mL) for 5 days. (A) The transfected CD4+ T cells were harvested on day 5, and the transfection efficiencies of LV-TOB1 and LV-shTOB1 were confirmed by qRT-PCR, and (B-H) qRT-PCR was performed to determine the mRNA expression of IFN-γ, IL-17A, TNF-α, T-bet, RORC, Foxp3, and IL-10, respectively, in these CD4+ T cells. (I-L) The culture supernatants of these transfected CD4+ T cells were also collected for detecting the levels of IFN-γ, IL-17A, TNF-α, and IL-10, respectively, using ELISA (M-O). LP-CD4+ T cells isolated from inflamed colon tissues of A-CD patients (n = 5), A-UC patients (n = 5) and normal colon tissues of 5 patients who underwent colectomy for colon cancer, respectively, were transfected with LV-TOB1, LV-shTOB1, and LV-NC, respectively, and then cultured under stimulation with plate-bound anti-CD3 mAb (5 μg/mL) and soluble anti-CD28 mAb (2 μg/mL) for 48 hours. IFN-γ, IL-17A, and TNF-α were detected by ELISA in the culture supernatants of these transfected LP-CD4+ T cells. Statistical analysis was performed with unpaired 2-sided Student’s t tests. ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, and ∗∗∗P < .001 vs LV-NC from the same group.