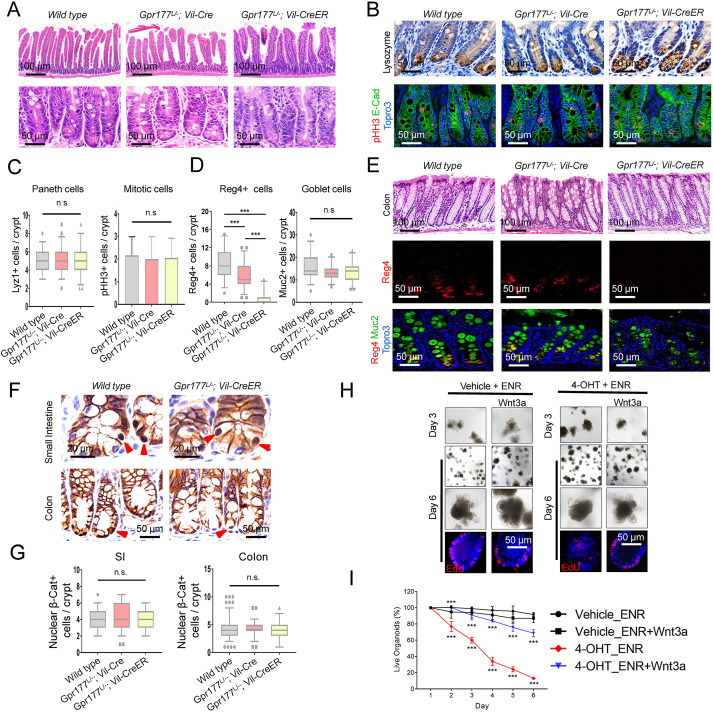
Fig. 1.
Inhibition of epithelial Wnts impaired colonic Reg4+ cell differentiation. (A) Histology of Gpr177L/−;Vil-Cre and Gpr177L/−;Vil-CreER mouse small intestines was the same as wild-type controls. (B) Immunohistochemistry for lysozyme and pHH3 showed normal Paneth and mitotic cells. (C) The numbers of Paneth or mitotic cells per crypt were not changed (n=3 mice per genotype). (D) The numbers of Reg4+ deep crypt secretory (DCS) colonic cells, but not goblet cells, were significantly decreased in Gpr177L/−;Vil-Cre and Gpr177L/−;Vil-CreER mouse colons (n=3 mice per genotype). (E) Histology and Reg4/Muc2 staining showed reduced Reg4+ cells in Gpr177L/−;Vil-Cre and Gpr177L/−;Vil-CreER mouse colons. (F) Immunohistochemistry for β-catenin showed unchanged nuclear β-catenin-positive cells in Gpr177L/−;Vil-Cre and Gpr177L/−;Vil-CreER mouse small intestinal or colonic crypts. (G) The numbers of nuclear β-catenin-positive cells per crypt were not changed (n=3 mice per genotype). (H) Gpr177L/−;Vil-CreER mouse enteroids cultured in ENR medium were treated with 4-OHT to delete Gpr177. Bright-field and fluorescent EdU images represented day 3 and 6 after 4-OHT or vehicle treatment, in the presence of exogenous Wnt3a. Wnt3a notably enhanced survival at day 6 when compared with vehicle group. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (I) Numbers of viable enteroids were counted daily following 4-OHT treatment. Wnt3a notably enhanced the survival of 4-OHT-treated enteroids when compared with no Wnt groups. Statistical significance provided for 4-OHT_ENR+Wnt3a versus 4-OHT_ENR and 4-OHT_ENR versus Vehicle_ENR. ***P<0.001. Data are mean±s.e.m. from at least three independent experiments. Also see Fig. S1.