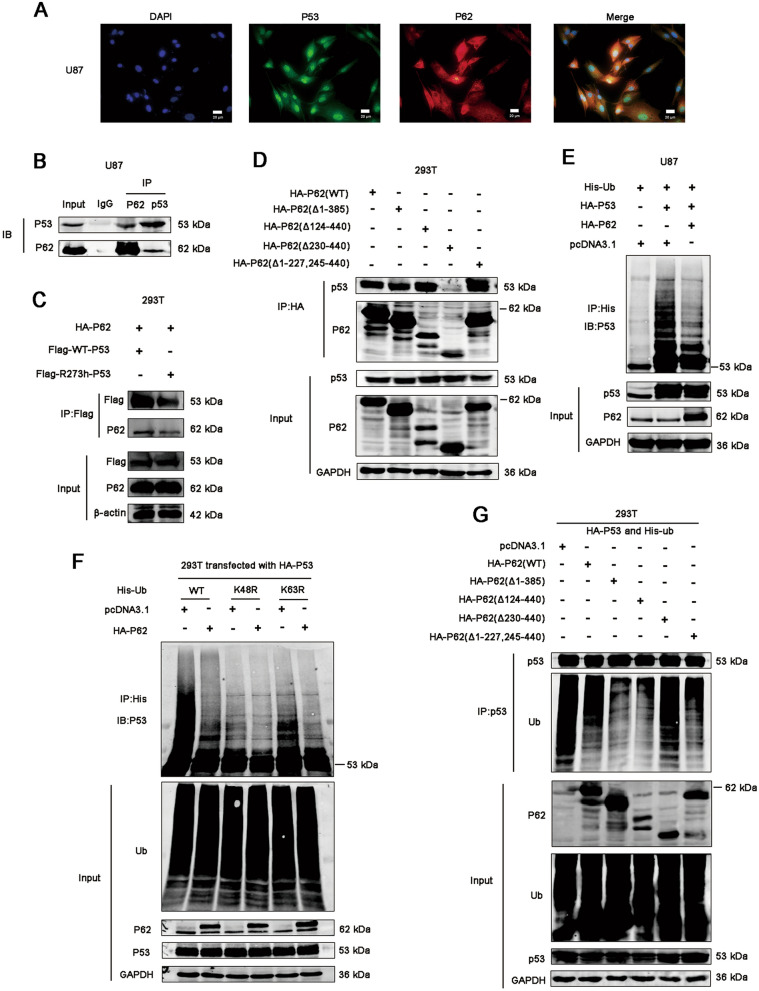
Fig. 3.
P62 associates with p53 and inhibits its ubiquitination. A The localization of p62 and p53 was detected by immunofluorescence in U87 cells. B Co-immunoprecipitation assays were performed to assess the association between p62 and p53. Lysates of U87 cells were subjected to IP using anti-P62 or anti-P53 antibodies, followed by immunoblotting with anti-P62 and anti-P53 antibodies. Non-specific IgG was used as a control. Whole cell lysates were used as an input control. C 293 T cells were transfected with flag-WT-p53 or flag-R273h-p53 plasmids together with HA-P62 plasmids. The proteins were immunoprecipitated from cell extracts using anti-Flag antibody, followed by immunoblotting with anti-P62 antibodies. D 293 T cells were transfected with plasmids encoding wild-type p62 (HA-p62 wild type) or a p62 deletion mutant. The proteins were immunoprecipitated from cell extracts using anti-HA antibody, followed by immunoblotting with anti-P62 and anti-P53 antibodies. E Representative immunoblots of p53 and ubiquitinated p53 in U87 cells when p62 was upregulated or downregulated. The proteins were immunoprecipitated from cell extracts using anti-His antibody, followed by immunoblotting with anti-P53 antibodies. F 293 T cells were transfected with plasmids encoding HA-p53, pcDNA3.1 or HA-P62 together with His-ubiquitin or its indicated mutants (His-K48R-Ub, His-K63R-Ub). The proteins were immunoprecipitated from cell extracts using anti-His antibody, followed by immunoblotting with anti-P53 antibodies. G 293 T cells were transfected with plasmids encoding HA-p53 and His-ubiquitin together with HA-P62 or its indicated mutants. The proteins were immunoprecipitated from cell extracts using anti-P53 antibody, followed by immunoblotting with anti-P62 and anti-Ubiquitin antibodies