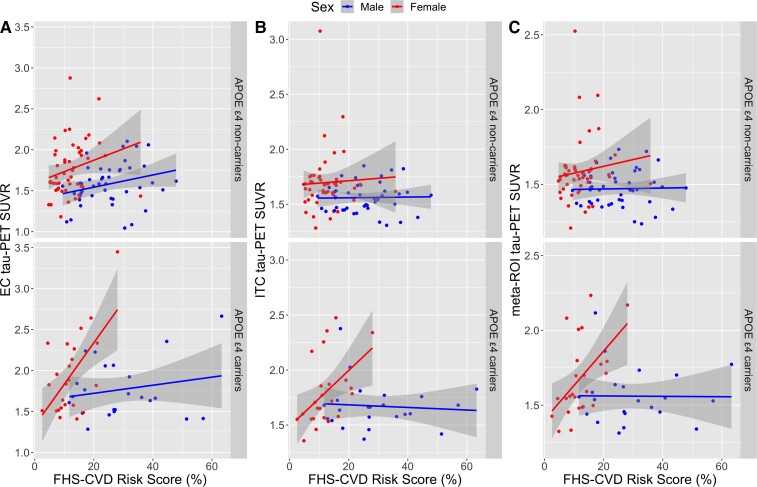
Figure 2.
Sex and APOE ɛ4 modify associations between cardiovascular disease risk and tau deposition. Scatter plots depicting sex differences in associations between FHS-CVD risk score and tau deposition in the (A) entorhinal cortex, (B) inferior temporal cortex and (C) a composite temporal lobe meta-ROI, among APOE ɛ4 non-carriers (top) and APOE ɛ4 carriers (bottom). Shaded regions represent 95% confidence intervals. We found significant interactions between sex and FHS-CVD risk on tau deposition in the EC (β = 0.05; 95% CI, 0.02–0.08; P = 0.001), ITC (β = 0.03; 95% CI, 0.01–0.05; P = 0.009) and meta-ROI (β = 0.02; 95% CI, 0.01–0.04; P = 0.008) among APOE ɛ4 carriers (bottom) but not among non-carriers (top).