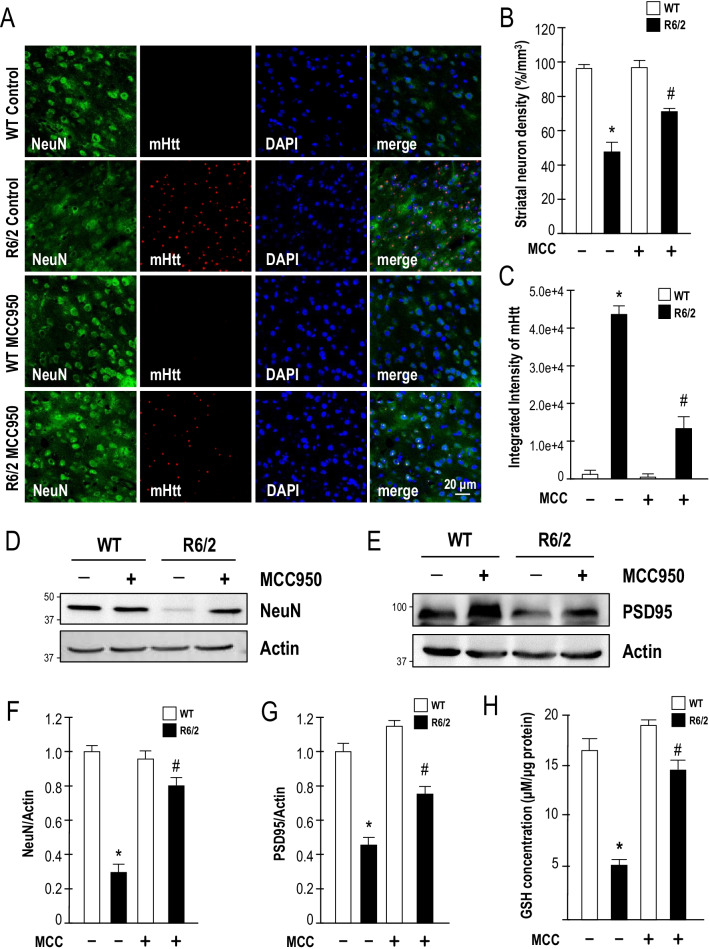
Fig. 4.
MCC950 significantly reduces neuronal loss and mHTT aggregation in a transgenic mouse model (R6/2) of HD. Mice were treated daily with MCC950 (10 mg/kg of body weight; oral administration) or water for 5 weeks from the age of 7 weeks. A Brain sections of 12-week-old mice were stained for NeuN and EM48. The number of neurons (as identified by the expression of NeuN; green) and the level of mHTT aggregation (EM48; red) in the striatum of the indicated mice (water-treated WT mice [n = 6], water-treated R6/2 mice [n = 6], MCC950-treated WT mice [n = 6], and MCC950-treated R6/2 mice [n = 6]) were quantified. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). The histograms show the number of striatal neurons (B) and the integrated intensity of mHTT (C). At least 500 cells from each animal were counted. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. Scale bars, 20 μm. *P < 0.05, between WT and R6/2 mice; #P < 0.05 vs. water-treated R6/2 mice. D–G Striatal lysates were analyzed using Western blot analysis. The molecular mass is indicated in kilodaltons. Results were normalized to those of actin. *P < 0.05, between WT and R6/2 mice; #P < 0.05 vs. water-treated R6/2 mice. H Striatal lysates were analyzed using a glutathione assay. *P < 0.05, between WT and R6/2 mice; #P < 0.05 vs. water-treated R6/2 mice