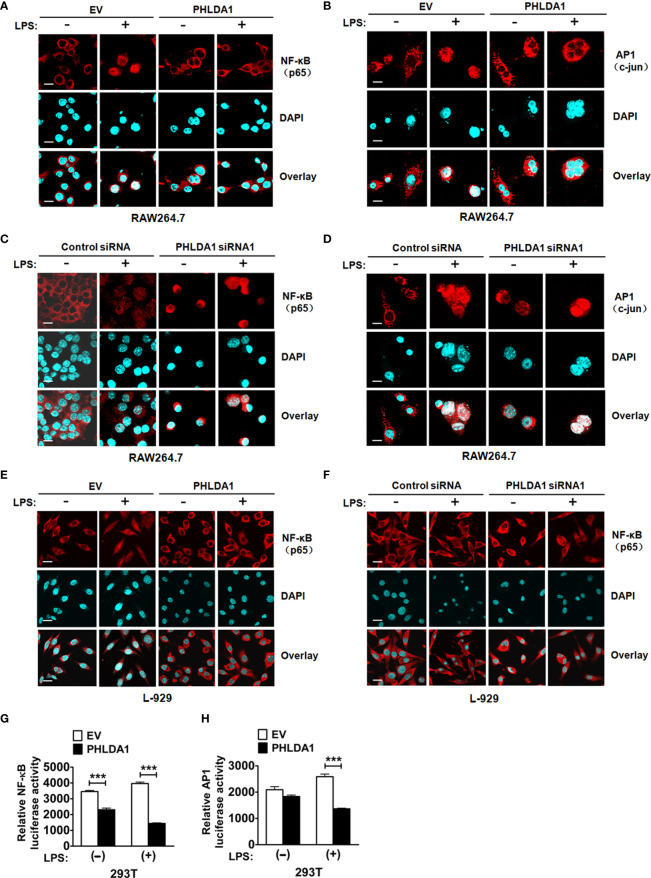
Figure 4.
PHLDA1 attenuates LPS-initiated nuclear translocations and responsive element activities of NF-κB and AP1. RAW264.7 cells (A, B) and L-929 cells (E) were transfected with EV or PHLDA1 plasmid, and then stimulated with or without LPS (0.1 μg/ml) for 1 h. Cells were immunostained with anti-NF-κB (p65) antibody or anti-AP1 (c-jun) antibody and Alexa-594-labeled secondary antibodies. The nuclei were stained with DAPI for 15 min. The merged images were captured with a confocal microscope (scale bar, 20 μm). RAW264.7 cells (C, D) and L-929 cells (F) were transfected with Control siRNA or PHLDA1 siRNA1, and then stimulated with or without LPS (0.1 μg/ml) for 1 h. Cells were immunostained with anti-NF-κB (p65) antibody or anti-AP1 (c-jun) antibody and Alexa-594-labeled secondary antibodies. The nuclei were stained with DAPI for 15 min. The merged images were captured with a confocal microscope (scale bar, 20 μm). (G, H) EV or PHLDA1 plasmid was transfected into 293T cells together with pTK–Renilla luciferase and NF-κB luciferase reporter plasmids. After 24 h of culture, the cells were incubated with LPS (0.1 μg/ml) for 20 h. The Dual-Luciferase® Reporter (DLR™) Assay System was performed to measure NF-κB or AP1 luciferase activity. Data are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments (***P < 0.001).