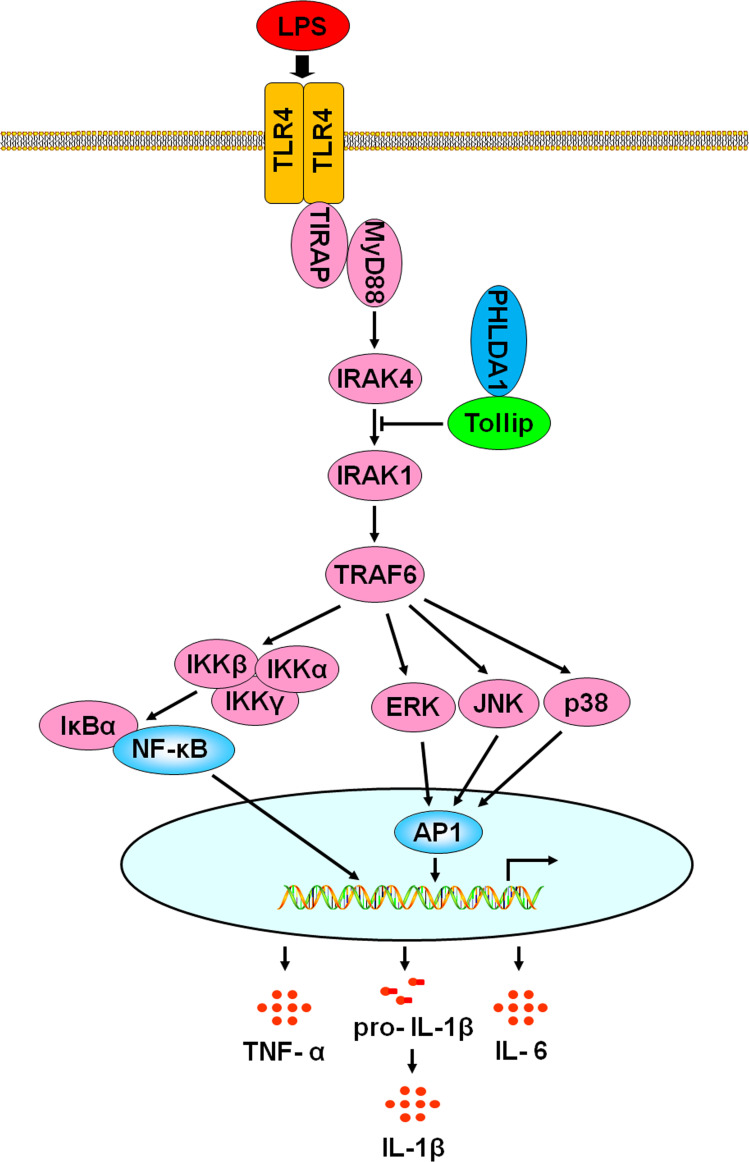
Figure 7.
A schematic representation of the role of PHLDA1 in modulating TLR4-mediated proinflammatory cytokine production via Tollip. After LPS-induced TLR4 activation, PHLDA1 recruited Tollip to inhibit IRAK phosphorylation, which further decreased the phosphorylation levels of some signal molecules (ERK, JNK, p38, IKKα/β, IκBα, and NF-κB subunit p65), the abilities of NF-κB and AP1 nuclear translocations, and their responsive element activities. Eventually, LPS-initiated proinflammatory cytokine production was repressed.