Table 1.
Dectin-1 ligands described up to date.
| Ligand | Structure | Pathology | Recognized by | Physiological relevance | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-glucans |
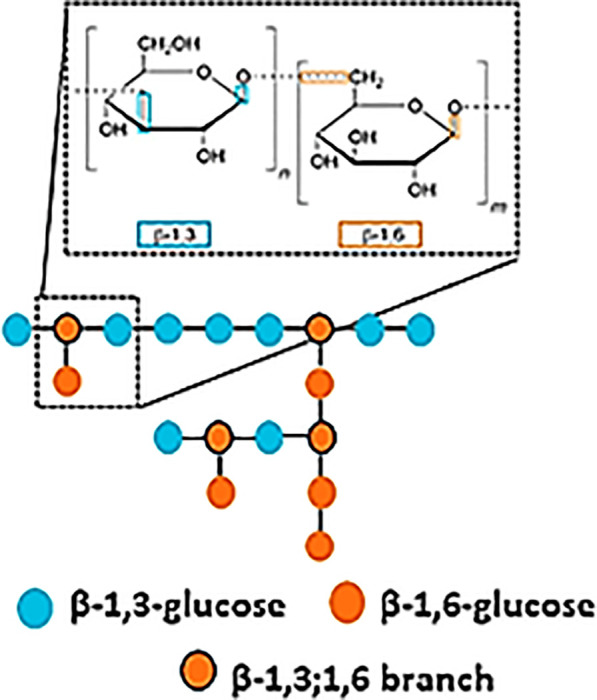
|
Microbial infections | Neutrophils | Proinflammatory: IL-1β, IL-6, IL-23, TNF-α and ROS production. | (20, 24–28) |
| Macrophages | Phagocytosis of pathogens. | ||||
| Monocytes | |||||
| Dendritic cells | |||||
| Keratinocytes | |||||
| Epithelial cells | |||||
| Galectin-9 |
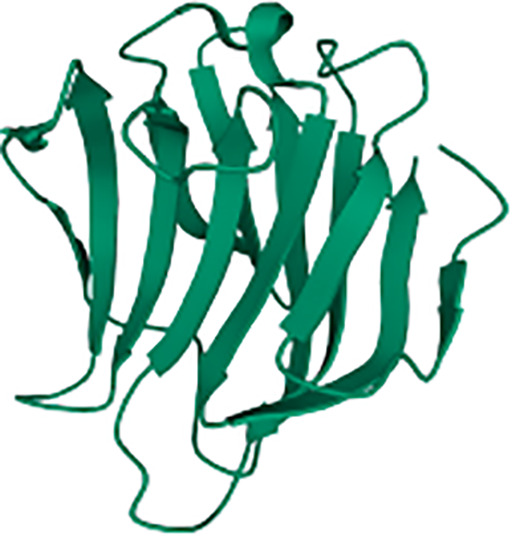
|
Autoimmune diseases | Neutrophils | Anti-inflammatory: tolerance and induction of oncostatin M overexpression. | (32) |
| Macrophages | |||||
| Microglia | |||||
| Dendritic cells | |||||
| Cancer | Macrophages | Immune tolerance: low MHC-II, iNOS and TNF-α, high CD206 expression. | (33) | ||
| Tumor progression. | |||||
| Annexins |
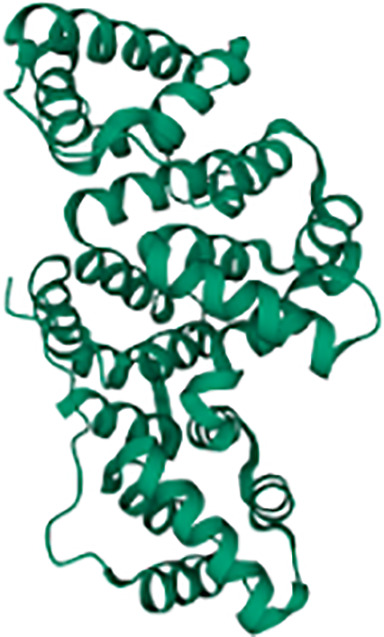
|
Autoimmune diseases and aging | Dendritic cells | Immune tolerance: reduced ROS production, dampening CD80 and CD86 production. | (34) |
| Vimentin |

|
Atherosclerosis | Myeloid cells | Proinflammatory. | (35) |
| Ischemia/reperfusion | Macrophages | Proinflammatory. | (36) | ||
| Neutrophils | M1-macrophage recruitment, myocardial injury, and apoptosis. | ||||
| Obesity | Macrophages | Proinflammatory: insulin resistance. | (37) | ||
| Tropomyosin |
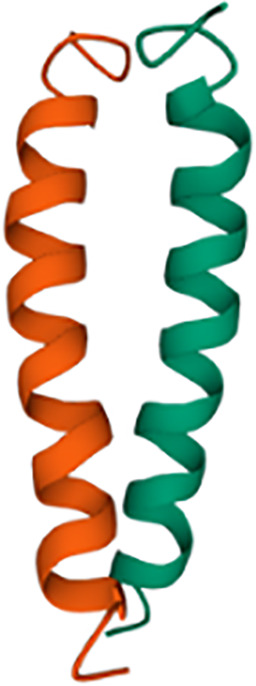
|
Allergy | Epithelial cells | Immune tolerance: reduced allergic symptoms and IL-33 dampening. | (38) |
| N-glycan |
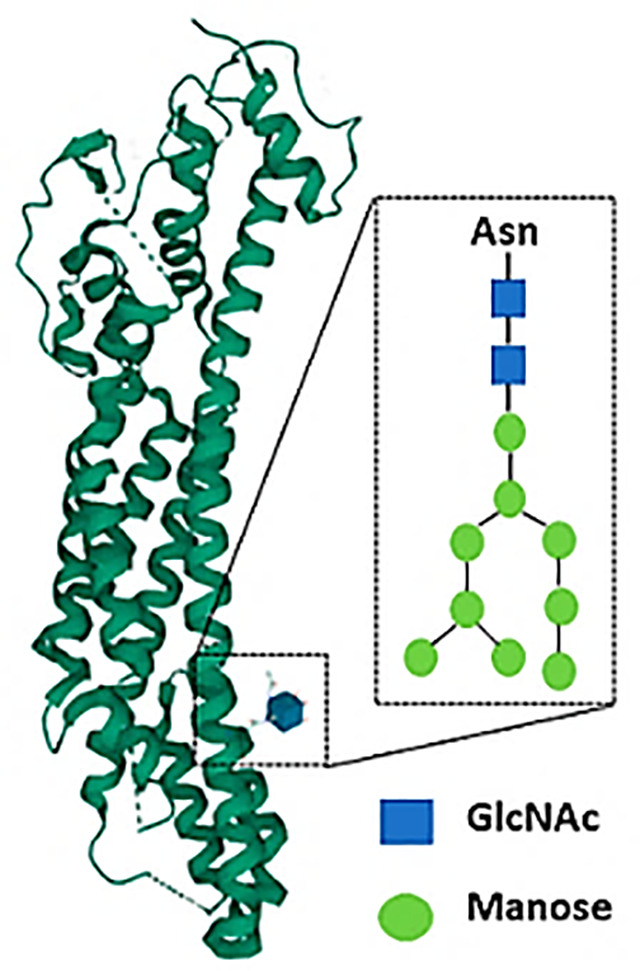
|
Cancer | Dendritic cells | Proinflammatory: Anti-tumor response via induction of natural killer cells cytolytic capacity. | (39, 40) |
| Macrophages |
