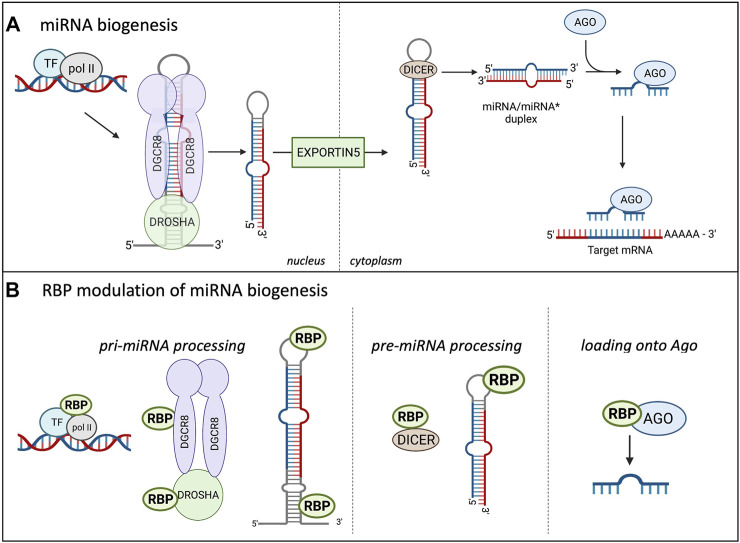
FIGURE 1.
Canonical miRNA biogenesis in Eukaryotes and the influence of RBPs. (A) shows the miRNA biogenesis in eukaryotes. miRNAs are transcribed in the nucleus by RNA polymerase II (pol II), creating the pri-miRNA, two sequential cleavage reactions follow. The microprocessor consists of Drosha and DGCR8 and performs the first cleavage reaction in the nucleus, creating the pre-miRNA. The pre-miRNA is transported into the cytoplasm through Exportin5 where the second cleavage reaction occurs. Dicer cleaves the terminal loop of the pre-miRNA, creating the miRNA/miRNA* duplex. The miRNAs are incorporated into the Ago protein, forming the minimal effector RNA induced silencing complex (miRISC) and target mRNA sequences. (B) Highlights the modulation of miRNA biogenesis by RBPs. RBPs can bind to the promoter region of certain miRNAs and influence their transcription. RBPs modulate miRNA expression at the pri-miRNA processing level through binding to Drosha and enhance or repress the cleavage. RBPs can also bind to the terminal loop or other sequences in the pri- and pre-miRNAs to influence the cleavage reactions. Additionally, RBPs can bind to DICER and influence this cleavage reaction through modulating DICER expression and availability. Lastly, RBPs can bind to AGO and increase the miRNA loading onto the AGO, increasing the miRISC silencing.