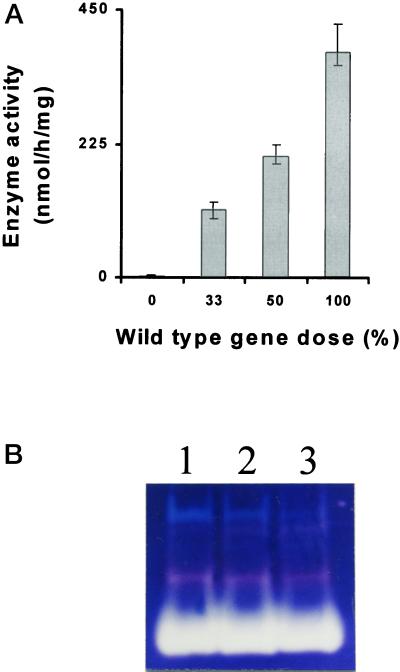
Figure 10.
Gene dosage. A, Gene dosages ranging from 0% wild-type alleles (homozygous mutant) to 100% wild type (homozygous wild-type); 50% corresponds to the heterozygous diploids, whereas 33% corresponds to a sta7/sta7/+ triploid. Histograms representing means and sds (n = 3) were calculated for each gene dose. One hundred micrograms of proteins from the different genotypes was used to assay isoamylase in the presence of 10 mm EDTA. Results are displayed as nanomoles of maltotriose equivalents produced from glycogen per hour and per milligram of protein. Total phosphoglucomutase-specific activities were monitored as internal controls and proved similar in all constructs (2.3 ± 0.5 nmol Glc-6-P formed from Glc-1-P min−1 mg−1 protein). B, Starch-containing zymograms. Fifty micrograms of crude extracts proteins from wild-type haploid strain A35 (lane 1), heterozygous diploid sta7/+ (lane 2), and heterozygous triploid sta7/sta7/+ (lane 3), were denatured and loaded on the same starch-containing zymogram according to the procedure described in Mouille et al. (1996). After renaturation, enzymes activities were revealed after incubation by staining the gel with a freshly made solution of iodine (0.2% [w/v] KI and 0.02% [w/v] I2).