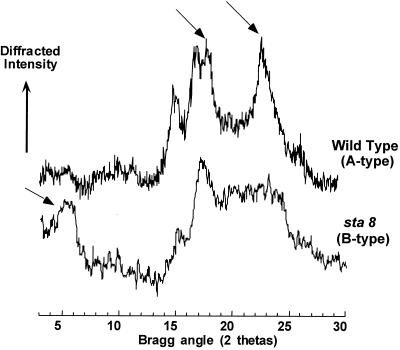
Figure 6.
X-ray diffraction of wild-type and mutant starches. Powder x-ray diffractograms of the starches extracted from the wild type (strain 330) and mutant (strain BafV13). Crystalline lattices of vascular plant starches fall into three types. The A type defines cereal endosperm starches, the B type is found in tuber starches and some high amylose mutant starches (for review, see Buléon et al., 1998). The C type is found in pea embryos and is a mix of the A and B type. The organization of the glucan double helical structures are completely different in A and B type starches. The arrows display the individual reference peaks that define the A type or the B type evidenced, respectively, in the wild-type and mutant starches.