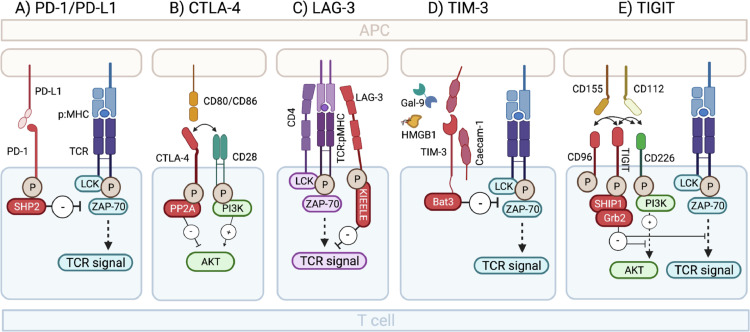
Figure 2.
Immune checkpoint inhibition: Receptor/ligand interaction and signaling. (A) PD-1-PD-L1/PD-L2 interaction signals through the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 (Src homology 2 domain-containing tyrosine phosphatase 2), which dephosphorylates kinases and blocks proximal TCR signal transduction. (B) Upon binding CD80/CD86 the cytoplasmatic tail of CTLA-4 transduces a signal through the protein phosphatase 2A (PPA2) to inhibit phosphorylation of Akt and thereby interfering with IL-2 production, cell cycle progression and proliferation. (C) LAG-3 is believed to signal through its unique KIEELE motive to transduce antiproliferative signals from the TCR. However, the intracellular proteins that bind the KIEELE motif and the signalling pathways further downstream are still not known. (D) Upon Caecam-1 and Gal-9/TIM-3 triggering, Bat3 gets released form the cytoplasmatic tail of TIM-3 and allows binding of SH2 domain containing Src kinases like LCK and ZAP-70 which subsequently block TCR signalling. (E) Upon ligand interaction, TIGIT becomes phosphorylated and recruitment of SHIP1 (SH2 domain containing inositol-5-phosphatase) and Grb2 (growth factor receptor bound protein 2) lead to blocking of PI3K (phosphatase 3-kinase) and MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) pathways resulting in reduced T-cell activation, proliferation, and effector functions.
PD-1: Programmed death-1; PD-L1: Programmed death ligand-1; CTLA-4: Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated protein 4 (CTLA-4); Lymphocyte activation gene 3; TIGIT: T-cell immunoglobulin and ITIM domain; TIM-3: T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin-domain containing-3 (TIM-3); TCR: T-cell receptor; LCK: lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase; ZAP-70: Zeta-chain-associated protein kinase-70; MHC: major histocompatibility complex.