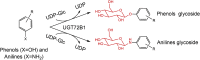
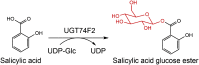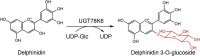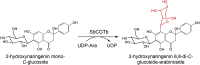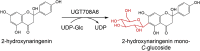| YjiC |
Bacillus subtilis |
NP_389104.1 |
7BOV |
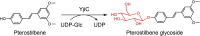 |
-
●
Ser277 is critical for Nucleoside Diphosphate (NDP) recognition
-
●
Glu317, Gln318, Ser128 and Ser129 are crucial for glycosyl moiety recognition
|
|
[129] |
| UGT72B1 |
Arabidopsis thaliana |
CAB80916.1 |
2VCE |
 |
-
●
His19 is positioned to act as a Brønsted base
-
●
Gln389 and Glu388 interact with the glucose moiety of donors
-
●
Glu83, Ile86, Leu118, Phe119, Phe148, Leu183, and Leu197 are predominant in the acceptor binding
|
– |
[130] |
| UGT74F2 |
Arabidopsis thaliana |
AAB64024.1 |
5U6M |
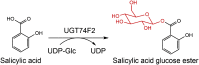 |
-
●
His18 shows a central role in catalysis
-
●
Tyr180 is important for ligand recognition or binding
-
●
Met274 could be crucial for orientation of the salicylic acid
|
– |
[131] |
| UGT89C1 |
Arabidopsis thaliana |
AAF80123.1 |
6IJ7 |
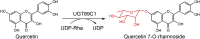 |
-
●
Asp356, His357, Pro147 and Ile148 are key residues for sugar donor recognition and specificity for UDP-β-l-rhamnose.
-
●
His21 is a key residue as the catalytic base and the only catalytic residue involved in catalysis.
|
|
[132] |
| UGT78K6 |
Clitoria ternatea |
BAF49297.1 |
3WC4 |
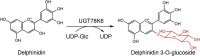 |
-
●
Pro78, Asp181 and Asp367 are involved in the acceptor binding.
-
●
Asn137 could participate in the recognition of the glucose moiety.
-
●
His17 is the key catalytic residue.
|
– |
[133,134] |
| UGT708C1 |
Fagopyrum esculentum |
BAP90360.1 |
6LLG |
 |
-
●
Asp382, Gln383, Thr151 and Thr150 play important role in the recognition of sugar moiety.
-
●
Phe130, Tyr102 and Phe198 bound and stabilize the acceptor.
-
●
Arg280 and Asp96 play important roles in the catalytic activity.
|
– |
[135] |
| GgCGT |
Glycyrrhiza glabra |
QGL05036.1 |
6L5P |
 |
-
●
R285, T145, D390 and Q391 determine the sugar donor preference.
-
●
The flopropione unit is the minimum required unit for the di-C-glycosylation due to the interactions of its 2’-/6′-OH with H27.
-
●
The spacious substrate-binding tunnel near G389 is critical for the di-C-glycosylation activity and the broad substrate promiscuity.
|
|
[48] |
| UGT73P12 |
Glycyrrhiza uralensis |
BBN60799.1 |
7C2X |
 |
|
– |
[136] |
| LpCGTa |
Landoltia punctata |
QLF98869.1 |
6LG1 |
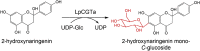 |
– |
– |
[76] |
| LpCGTb |
Landoltia punctata |
QLF98870.1 |
6LFN |
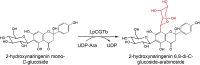 |
– |
– |
[76] |
| SbCGTa |
Scutellaria baicalensis |
QLF98861.1 |
6LG0 |
 |
|
– |
[76] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| SbCGTb |
Scutellaria baicalensi |
QLF98862.1 |
6LFZ |
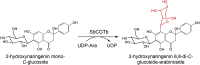 |
|
|
[76] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| UGT708A6 |
Zea mays |
ACF81582.1 |
6LF6 |
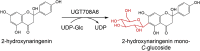 |
– |
– |
[76] |
| UGT71G1 |
Medicago truncatula |
AAW56092.1 |
2ACV |
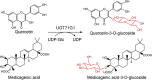 |
-
●
His22 is the catalytic base.
-
●
Asp121 is a key residue that may assist deprotonation of the acceptor.
-
●
Glu381 is the key residue in recognition of the sugar donor.
|
– |
[2] |
| UGT85H2 |
Medicago truncatula |
ABE87250.1 |
2PQ6 |
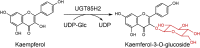 |
|
– |
[137] |
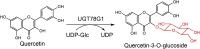
| UGT78G1 |
Medicago truncatula |
ABI94025.1 |
3HBF |
 |
-
●
Glu192 is the key residue for the reverse reaction.
-
●
His26 act as the catalytic residue.
-
●
Asp124 also plays an essential role in catalysis.
|
– |
[138] |
| Os79 |
Oryza sativa |
BAF14158.1 |
5TMB |
 |
-
●
His27 activate the trichothecene O3 hydroxyl for nucleophilic attack at C1’ of the UDP-glucose donor.
-
●
Thr291 plays a critical role in catalysis as a catalytic acid or to position the UDP moiety during the nucleophilic attack.
|
– |
[139] |
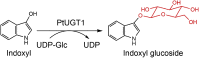
| PtUGT1 |
Persicaria tinctoria |
BBB06426.1 |
5NLM |
 |
-
●
E88 could play a major role in indoxyl specificity and turnover.
-
●
H26 is expected to be the Brønsted base.
-
●
D122 is believed to balance the charge on the catalytic histidine.
|
– |
[140] |
| PaGT2 |
Phytolacca americana |
BAG71125.1 |
6JEL |
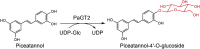 |
|
|
[42] |
| PaGT3 |
Phytolacca americana |
BAG71127.1 |
6LZX |
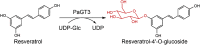 |
|
– |
[141] |
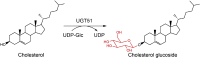
| UGT51 |
Saccharomyces cerevisiae |
AAB67475.1 |
5GL5 |
 |
-
●
Asp752 serve as a catalytic base.
-
●
Met851 is important for UGT51 activity.
-
●
Gln1094, Asp1093 and Ser1072 make several critical interactions with the glucose moiety of donor.
|
|
[142,143] |
| UGT74AC1 |
Siraitia grosvenorii |
AEM42999.1 |
6L8W |
 |
|
|
[144] |
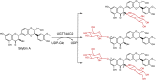
| UGT74AC2 |
Siraitia grosvenorii |
AXK92493.1 |
7BV3 |
 |
-
●
The uracil ring forms hydrogen bonds and parallel π-stacking interactions with A353 and W352, respectively, and the ribose ring interacts with the enzyme through hydrogen bonds with E378 and Q355, while the α-phosphate forms hydrogen bonds with H370, N374 and S375
-
●
The acceptor binding pocket is constructed by 13 residues, where P12, L43 and V91 are located at the entrance, and V190, M196 as well as L200 are situated at the bottom
|
-
●
Mutant G11Y is found that shows 75% selectivity and >99% conversion towards silybin A-3,7-O-diglucoside.
-
●
Three variants show enhanced regioselectivity toward silybin A-7-O-glucoside, P12Y (81% selectivity and 68% conversion), L200W (92% selectivity and 61% conversion) and Y145W (89% selectivity and 75% conversion)
|
[145] |
| UGT76G1 |
Stevia rebaudiana |
AAR06912.1 |
6INF |
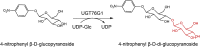 |
-
●
His25 is the general base, which deprotonates the 3-hydroxyl of the accepting glucose A to activate it as a nucleophile.
-
●
Asp124 plays an important catalytic role in relaying protons off and on His25.
|
– |
[146] |
| TcCGT1 |
Trollius chinensis |
QCZ42162.1 |
6JTD |
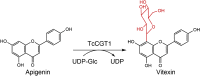 |
-
●
H24 acts to stabilize both the deprotonated substrate and the product sugar, though it is not indispensable for the glycosylation activity.
-
●
E396 plays an important role to stabilize and orient the UDP–Glc sugar.
|
|
[49] |
| VvGT1 |
Vitis vinifera |
AAB81683.1 |
2C1X |
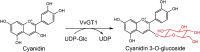 |
|
– |
[147] |
| UGTPg45 |
Panax ginseng |
AKA44586.1 |
– |
 |
– |
|
[148] |