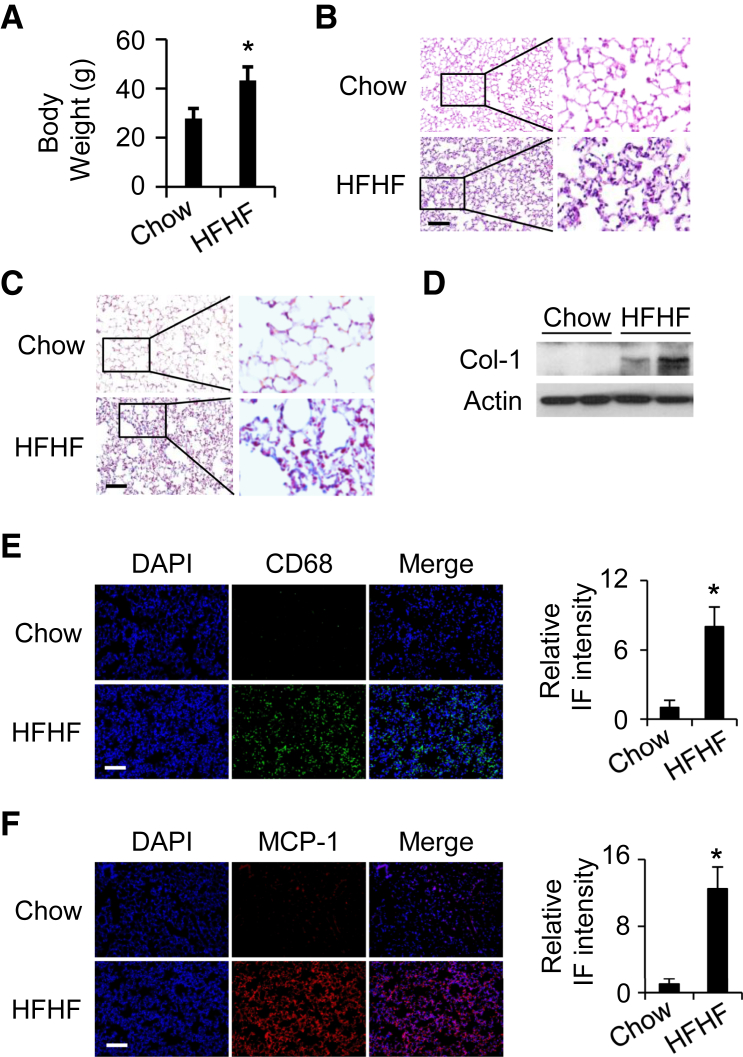
Figure 1.
Chronic high-fat and high-fructose (HFHF) diet-induced lung inflammation/injury in wild-type (WT) C57BL/6 mice. A: Body weight of WT C57BL/6 mice fed with normal chow or an HFHF diet for 20 weeks. B and C: Representative hematoxylin and eosin staining (B) and Masson’s staining (C) of lung tissues from WT mice fed a chow diet or an HFHF diet for 20 weeks. D: Lung tissues from WT mice fed a chow diet or an HFHF diet for 20 weeks were collected. Two representative samples for each group were loaded to detect collagen (Col-1) protein expression by Western blotting. Actin is a loading control. E and F: Immunofluorescence (IF) shows increased CD68 (green) (E) and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) (red) (F) expression in lung tissues from WT mice fed with chow or HFHF diet for 20 weeks. DAPI stained the nuclei (blue). The black boxes indicate the areas enlarged for view. Quantification of expression levels in E and F from 5 fields per slide per mouse and 3 mice per group. n = 6 to 8 (A). ∗P < 0.05 versus WT chow diet group. Scale bar = 100 μm.