Figure 2. The yeast growth phenotype is a readout for the kinase phosphotransferase activity.
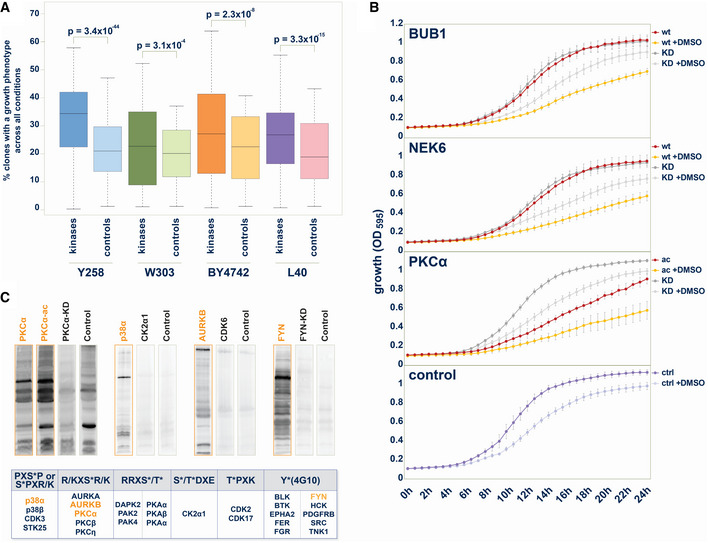
- Statistical comparison of the number of yeast growth phenotypes between kinase group and control protein group. In each strain, across all conditions, the percentage of kinases that cause a phenotype upon exogenous expression is significantly higher than the percentage of control proteins, that cause a growth phenotype upon overexpression. Data are from a single large‐scale growth measurement. The boxes extend from 1st to 3rd quartile with the central band representing the median. The whiskers extend to the furthest point up to 1.5 times the interquartile range away from the nearest quartile, with any further points marked as outliers. P‐values are calculated using the Mann–Whitney test.
- Growth comparisons of selected kinases with the kinase‐dead mutant match. 24 h growth curves (OD595) from liquid culture of yeast strains (W303) expressing human kinase in the presence or absence of 3.2% (v/v) DMSO. Upper panel: BUB1: BUB1 wild type, BUB1‐KD: BUB1(K821M); upper middle panel: NEK6: NEK6 wild type, NEK6‐KD: NEK6(K74M&K75M); lower middle panel: PKCα‐ac: PKCα(A25E), PKCα‐KD: PKCα(K368R); lower panel: Control with empty plasmid. Error bars represent SD from three biological replicates.
- Human protein kinases phosphorylate large sets of yeast proteins. Upper panel: In total, 27 human protein kinases showed activity toward yeast proteins visible on western blots through enhanced reactivity with phospho‐motif antibodies on yeast proteins in comparison to other human kinases, kinase‐dead mutant versions, or vector control samples. Commercially available pS/T‐antibodies with relatively low sequence specificities were chosen to enable detection of phosphorylation of the yeast proteome by human kinases. Lower panel: Examples of western blots with equal amount of whole yeast cell lysate from strains expressing human kinases loaded. When developed with the indicated phospho‐motif‐recognizing antibodies, immunoreactive bands indicated phosphorylation of yeast proteins.
