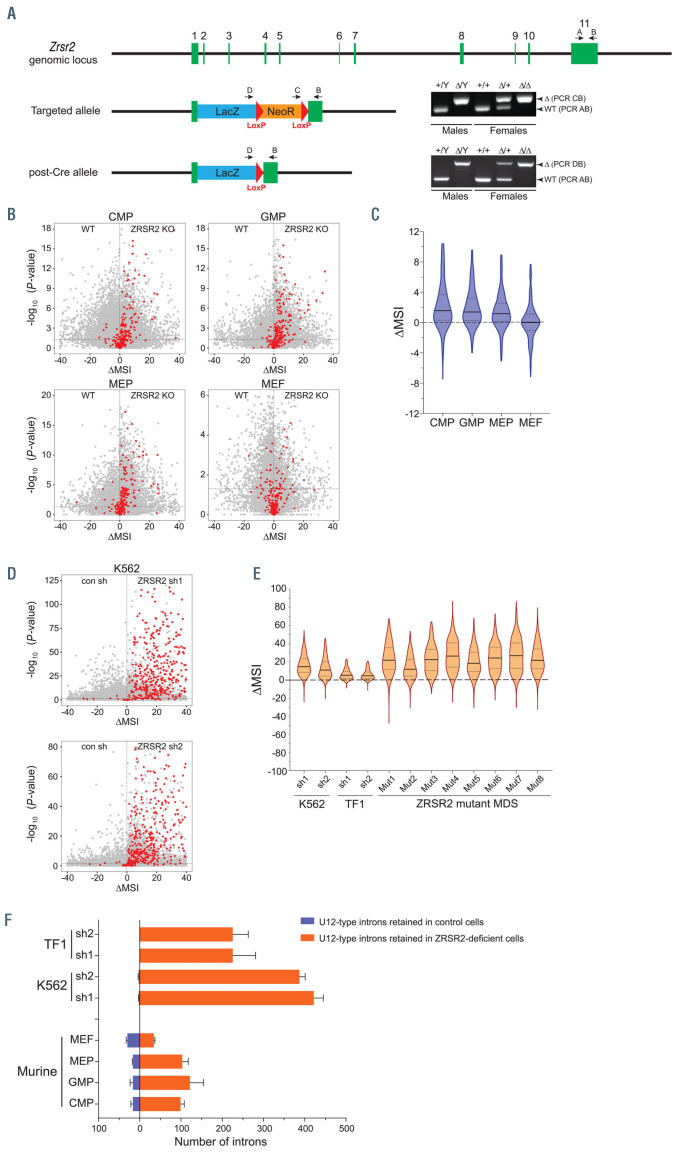
Figure 1.
Deficiency of ZRSR2 causes aberrant retention of U12- type introns in murine myeloid cells. (A) Generation of Zrsr2 knockout (KO) mice. Mice carrying the targeted Zrsr2 allele were crossed with CMV-Cre mice to excise the neomycin resistance cassette (post-Cre allele). Polymerase chain reaction analysis (right) shows genotyping of deleted Zrsr2 alleles in male and female mice. (B) Dot plots show intron retention in Zrsr2-deficent murine myeloid precursors (CMP, GMP and MEP) and MEF compared to wild-type (WT) cells. U12- type introns are depicted as red circles. (C) Range of DMSI values for retention of U12-type introns in murine cells. Outliers were removed from the plot using Gout method (Q=1). (D) Intron retention in ZRSR2 knockdown K562 cells (expressing either short hairpin RNA [shRNA] shRNA1 or shRNA2) compared to control transduced cells. (E) Range of DMSI values for intron retention (U12-type introns) in TF1, K562 and myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) bone marrow cells. Outliers were removed from the plot using Gout method (Q=1). RNA sequencing data of ZRSR2- deficient TF1 cells and ZRSR2 mutant MDS used in this analysis has been previously published.8 (F) Number of U12-type introns retained in murine and human cells lacking ZRSR2 (P<0.05; Fisher's exact test). CMP: common myeloid precursors; GMP: granulocyte monocyte precursors; MEP: megakaryocyte erythroid precursors; MEF: murine embryonic fibroblasts; MSI: mis-splicing index. Difference in MSI values (DMSI) was calculated as DMSI=MSIknockout−MSIwild-type.